Home » NEET Exam Pattern
Category Archives: NEET Exam Pattern
NEET 2021 Syllabus for Physics, Chemistry, and Biology
NEET 2021 syllabus by MCI covers concepts from class 11 and 12. Specifically, NEET syllabus consists of three subjects i.e. Physics, Chemistry, and Biology (Zoology and Botany). Consequently, the aspirants are advised to go through the NEET 2021 Zoology syllabus and NEET 2021 Botany syllabus. There have been rumours of the NEET 2021 syllabus reduction but as no official notification has been released by the concerned authorities so students should study according to the earlier syllabus.
- NEET syllabus 2021 will be conducted in offline mode where candidates will have to follow the NEET 2021 exam pattern as prescribed by the NTA.
- A total of 180 multiple choice questions are asked in the NEET 2021 question paper. Out of which, 90 questions are from Biology section, 45 questions from Physics, and 45 questions from Chemistry section.
- The total time allotted for attempting the NEET 2021 question paper will be 3 hours.
To get a high score and to secure the name in the top position of the merit list, the aspirants are advised to keep checking the essential topics during their NEET 2021 preparation accordingly. This article highlights the topic-wise and chapter-wise weightage apart from NEET Syllabus 2021.
Check the detailed NEET 2021 Exam Pattern
NEET Syllabus 2021
The NEET 2021 Syllabus by MCI is made as per the curriculum of NCERT books. Specifically, class XI and XII NCERT books play a vital role to clear major concepts and topics. Now, the mentioned table shows the detailed marking scheme for every subject.
| Examination | National Eligibility Entrance Test (NEET) |
| NEET Syllabus Issuing Authority | National Testing Agency |
| Physics | 45 questions |
| Chemistry | 45 questions |
| Biology | Botany Section: 45 questions and Zoology Section: 45 questions |
Read: Why NCERT Books are Important for NEET Exam?
NEET 2021 Section Wise Syllabus
The medical exam is conducted by NTA to measure the excellence of the candidates in Physics, Chemistry and Biology. For instance, go through the Subject Wise Preparation Tips of Physics
Unit 7: Thermodynamics
- First law of thermodynamics, Definition of temperature that is the concept of zeroth law of thermodynamics, thermal equilibrium, Isothermal and adiabatic processes, Heat, work and internal energy.
- Second law of the thermodynamics that is Reversible and irreversible processes.
- Heat engines and refrigerators.
Unit 8: Gravitation
- Escape velocity, orbital velocity of a satellite, Gravitational potential energy, Geostationary satellites, gravitational potential.
- The universal law of gravitation, Kepler’s laws of planetary motion, Acceleration due to gravity and its variation with altitude and depth.
Unit 9: Oscillations and Waves
- Wave motion, Displacement relation for a progressive wave, fundamental mode and harmonics, Longitudinal and transverse waves, reflection of waves, Doppler Effect, Principle of superposition of waves, and reflection of waves, speed of wave motion, Beats.
- Periodic functions, Periodic motion-period, Simple harmonic motion (SHM) and its equation, its phase, frequency, energy in SHM –Kinetic and potential energies, forced and damped oscillations ( qualitative ideas only), Periodic functions, simple pendulum- derivation of expression for its time period,free, resonance.
UNIT 10: Behavior of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory
- Kinetic energy and temperature, law of equipartition of energy (statement only) and application to specific heat capacities of gases, Kinetic theory of gases: Assumptions, concept of pressure, application to specific heat capacities of gases, degree of freedom, concept of gases,theory on mean free path.
- Equation of state of a perfect gas.
- Work done on compressing a gas.
Detailed NEET Physics Syllabus of Class XII
Unit 1: Current Electricity
- Kirchhoff’s laws and its simple applications, metre bridge and Wheatstone bridge.
- Carbon resistors, temperature dependence of resistance, series and parallel combinations of resistors, color code for carbon resistors.
- Measurement of internal resistance of a cell, Potentiometer theory and its application for estimating the probable distinction. In addition, to compare the emf of two cells.
- Combination of cells, parallely and also in series, Internal resistance of cell, potential difference of the emf of a cell.
- Ohm’s law, drift velocity and mobility, V-I characteristics (both linear and nonlinear), electrical resistivity, Electric current, electrical conductivity, flow of electric charges in a metallic conductor, electrical power and energy.
Unit 2: Electrostatistics
- Statement of Gauss’s theorem and its applications for finding the field due to infinitely long straight wire, Electrical flux, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet, uniformly charged thin spherical shell(field inside and outside)
- Dielectrics and electric polarization, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor (with and without dielectric medium between the plates), Conductors and insulators, capacitors and capacitance. Combined capacitors both in case of series and parallel, Van de Graff generator, Dielectrics and electric polarization, bound charges and free charges inside a conductor, energy stored in a capacitor.
- Electric field, electric dipole, torque on a dipole in a uniform electric field, electric field due to a point charge and due to a dipole, electric field lines.
- Coulomb’s law-force between two point charges, superposition principle, Electric charges and their conservation, forces between multiple charges, Constant charge distribution.
- Electric potential due to a point charge, Electric potential, electrical potential energy of a system of two point charges, electric potential energy of electric dipoles in an electrostatic field, a dipole and system of charges: equipotential surfaces.
Unit 3: Alternating Currents and Electromagnetic Induction
- LC oscillations (qualitative treatment only), power in AC circuits, Alternating currents, peak and rms value of alternating current/voltage, LCR series circuit, wattles current, resonance, reactance and impedance.
- AC generator and transformer.
- Faraday’s law, induced emf and current, Self and mutual inductance, Eddy currents, Lenz’s law, Electromagnetic induction.
Unit 4: Magnetic Effects of Magnetism and Current
- Ampere’s law and its application for infinitely long straight wire, Cyclotron, Force on a moving charge in uniform electric and magnetic fields, toroidal and straight solenoids.
- Magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole( that is bar magnet) along with the axis and perpendicular to axis, Earth’s magnetic element and magnetic field, Torque on a magnetic dipole that is bar magnetic (it is in a uniform magnetic field), Current loop as a magnetic dipole, magnetic dipole moment of current loop, Magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron, bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid, magnetic field lines.
- Permanent magnets, Electromagnetic and the factors affect its strength.
- Biot –Savart law and its application for carrying current in a circular loop, Concept of magnetic field, and Oersted’s experiment.
- Ferro-magnetic, diamagnetic and paramagnetic substances. Read the examples.
- Torque experienced by a current loop in a magnetic field, Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field. Moving coil galvanometer as conversion and current sensitivity to voltmeter and ammeter, Force between two parallel current-carrying conductors, definition of ampere.
Unit 5: Optics
- Reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset and scattering of light-blue colour of the sky
- Magnification, mirror, power of a lens and combination of thin lenses in contact combination of a lens.
- Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror formula.
- Refraction and dispersion of light through a prism, tital internal reflection and its applications optical fibres.
- Refraction at spherical surfaces, lenses, lens-maker’s formula, thin lens formula.
- Astronomical and microscopes telescopes (reflecting and refracting); magnifying powers.
- Resolving power of microscopes and astronomical telescopes.
- Polarization, Brewster’s law, plane polarized light; Uses of Polaroids and plane polarized light.
- Using Huygens’ principle, proof of laws of reflection and refraction.
- Using lenses, correction of myopia and hypermetropia
- Optical instruments: Human eye, image formation and accommodation.
- Wave optics: Huygens’ principle and Wavefront, reflection and refraction of plane wave at a plane surface using wavefronts.
- Width of central maximum, diffraction due to single slit
- Interference.
- Coherent sources and sustained interference of light
- Young’s double hole experiment
- Expression for fringe width
Unit 6: Electromagnetic Waves
- Electromagnetic spectrum (microwaves, radio waves, visible, infrared, ultraviolet, gamma rays, x-rays) including elementary facts about their uses.
- Need for displacement current
- Transverse nature of electromagnetic waves
- Electromagnetic waves and their characteristics (qualitative ideas)
Unit 7: Atoms And Nuclei
- Mass-energy relation, binding energy per nucleon, mass defect and its variation with mass number
- Nuclear fission and fusion
- Radioactivity – alpha, beta and gamma particles
- Rays and their properties decay law.
- Composition and size of nucleus, atomic masses, isobars, isotopes, isotones.
- Bohr model, Alpha-particle scattering experiments, Rutherford’s model of atom, Energy levels, hydrogen spectrum
Unit 8: Dual Nature Of Matter And Radiation
- Davisson-Germer experiment (omit experimental details, only conclusion should be explained)
- Matter waves – Wave nature of particles
- De Broglie relation
- Hertz and Lenard’s observations, Photoelectric effect, Einstein’s photoelectric equation-particle nature of light
Unit 9: Electronic Devices
- Junction transistor, characteristics of a transistor, transistor action, transistor as an amplifier (common emitter configuration) and oscillator
- Logic gates (OR, AND, NOT, NAND and NOR)
- Transistor as a switch
- Energy bands in solids (qualitative ideas only), conductors, insulators and semiconductor diode- I-V characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as a rectifier, I-V characteristics of LED, photodiode, solar cell
- Zener diode
- Zener diode as a voltage regulator
Click here for Detailed Physics Syllabus
NEET Syllabus 2021: Chemistry
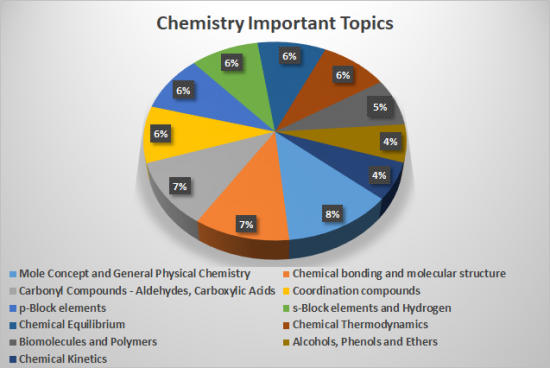
The Chemistry syllabus of NEET is quite broad and there are a total of 30 chapters. Among those, 14 chapters are from class XI syllabus and 16 chapters are from Class XII syllabus. Candidates also check the name of the chapters from which Chemistry questions are asked mostly in NEET exam.
| Chapters from Class XI | Chapters from Class XII |
| Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Solid State |
| Structure of Atom | Solutions |
| Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Electrochemistry |
| Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Chemical Kinetics |
| States of Matter: Gases and Liquids | Surface Chemistry |
| Thermodynamics | General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements |
| Equilibrium | p- Block Elements |
| Redox Reactions | d and f Block Elements |
| Hydrogen | Coordination Compounds |
| s-Block Elements (Alkali and Alkaline earth metals) | Haloalkanes and Haloarenes |
| Some p-Block Elements | Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers |
| Organic Chemistry- Some Basic Principles and Techniques | Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids |
| Hydrocarbons | Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen |
| Environmental Chemistry | Biomolecules |
| – | Polymers |
| – | Chemistry in Everyday Life |
Detailed NEET Chemistry Syllabus of Class XI
Unit 1: Structure of Atom
- Concept of shells and subshells
- Dual nature of matter and light
- De Broglie’s relationship
- Heisenberg uncertainty principle
- Concept of orbital, quantum numbers
- Shapes of s,p and d orbitals
- Aufbau principle
- Atomic number, isotopes and isobars
- Hund’s rule and Pauli exclusion principles, electronic configuration of atoms
- Stability of half filled and completely filled orbitals.
Unit 2: Basic Fundamental Concepts of Chemistry
- General Introduction: Important and scope of chemistry
- Atomic and molecular masses
- Mole concept and molar mass; chemical reactions, stoichiometry and calculations based on stoichiometry; percentage composition and empirical and molecular formula;
- Dalton’s atomic theory: concept of elements, atoms and molecules, Laws of chemical combination.
Unit 3: Molecular Structure and Chemical Bonding
- Lewis structure, polar character of covalent bond, resonance, geometry of molecules, valence bond theory.
- VSEPR theory
- Concept of hybridization that involves s, p and d orbitals
- Shapes of some simple molecules
- Molecular orbital theory: homonuclear diatomic molecules (only qualitative idea)
- Valence electrons, ionic bond, covalent bond, bond parameters
- Hydrogen bond
Unit 4: Periodicity in Properties and Classification of Elements
- Modern periodic law and long form of periodic table, periodic trends in properties of elements- atomic radii, electronegativity, valence, ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy.
Unit 5: Thermodynamics
- Introduction of entropy as state function
- Second law of thermodynamics
- Gibbs energy change for spontaneous and non-spontaneous process
- Criteria for equilibrium and spontaneity
- First law of thermodynamics-internal energy and enthalpy, heat capacity and specific heat, measurement of U and H, Hess’s law of constant heat summation, phase transition, ionization, solution and dilution, enthalpy of: bond dissociation, combustion, formation, atomization, sublimation.
- Brief introduction on Third law of thermodynamics.
Unit 6: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids
- Kinetic energy and molecular speeds (elementary idea),
- Liquefaction of gases, deviation from ideal behavior, critical temperature
- Ideal gas equation, Avogadro number
- Liquid State- Surface tension (qualitative idea only, no mathematical derivations) vapour pressure, and viscosity.
- Role of gas laws of elucidating the concept of the molecule, Boyle’s law, Charle’s law, Gay Lussac’s law, Avogadro’s law, ideal behavior of gases
- Three states of matter, intermolecular interactions,
- Types of bonding, melting and boiling points
- Empirical derivation of gas equation
Unit 7: Redox Reactions
- Concept of oxidation and oxidation and reduction
- Redox reactions, oxidation number
- Balancing redox reactions in terms of gain and loss of electron
- Change in oxidation numbers
Unit 8: Equilibrium
- Hydrolysis of salts (elementary idea)
- Buffer solutions
- Henderson equation, common ion effect (with illustrative examples), solubility product
- Factors affecting equilibrium-Le Chatelier’s principle
- Ionic equilibrium – ionization of acids and bases, weak and strong electrolytes, ionization of polybasic acids, degree of ionization, acid strength, concept of PH
- Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes
- Dynamic nature of equilibrium
- Law of chemical equilibrium, equilibrium constant
Unit 9: s-Block Elements (Alkali and Alkaline earth metals)
- Preparation and Properties of Some important Compounds: chemical reactivity with oxygen, water, hydrogen and halogens; uses.
- Industrial use of lime and limestone, biological importance of Mg and Ca and potassium
- General introduction, occurrence, electronic configuration, anomalous properties of the first element of each group
- Group I and group 2 elements: Diagonal relationship, trends in Sodium carbonate, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide and sodium hydrogen carbonate, trends in the variation of properties (such as ionization enthalpy, atomic and ionic radii), biological importance of sodium
Unit 10: Hydrogen
- Physical and chemical properties of water, heavy water
- Hydrogen peroxide – preparation, uses, reactions, and structure
- Occurrence, preparation, isotopes, properties and uses of hydrogen
- Hydrides-ionic, covalent and interstitial
Unit 11: Some Basic Principles and Techniques on Organic Chemistry
- Electronic displacements in a covalent bond: electromeric effect, inductive effect, hyperconjugation and resonance
- General introduction, methods of purification qualitative and quantitative analysis
- Heterolytic fission and Homolytic of a covalent bond: free radials, carbocations, carbanions;
- Electrophiles and nucleophiles
- Types of organic reactions
- Classification and IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds
Unit 12: Some p-Block Elements
- General Introduction to p-Block Elements
- Important compounds of silicon their uses: silicates and zeolites, silicon tetrachloride, silicones, their uses
- Group 13 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, variation of properties, oxidation states, Boron, some important compounds: borax, boric acids, boron hydrides, trends in chemical reactivity, anomalous properties of the first element of the group; Aluminium: uses, reactions with acids and alkalis
- General 14 elements: General introduction, trends in chemical reactivity, anomalous behavior of the first element, electronic configuration, occurrence, variation of properties, oxidation states. Carbon, allotropic forms: uses of some important compounds: oxides physical and chemical properties
Also check | NEET 2021 Preparation Tips for Chemistry
Unit 13: Environmental Chemistry
- Environmental pollution: Air, soil and water pollution, chemical reactions in atmosphere, smogs, major atmospheric pollutants
- Acid rain ozone and its reactions
- Effects of depletion of ozone layer
- Greenhouse effect
- Global warming – pollution due to industrial wastes
- Green chemistry as an alternative tool for decreasing pollution
- Strategy for control of environmental pollution
Unit 14: Hydrocarbons
- Alkynes: Nomenclature, chemical reactions, structure of triple bond (ethyne): acidic character of alkynes, addition reaction of – hydrogen, halogens, physical properties, methods of preparation, hydrogen halides and water.
- Alkanes: Nomenclature,conformations (ethane only), isomerism, physical properties, combustion and pyrolysis, chemical reactions including free radical mechanism of halogenation
- Aromatic hydrocarbons: Introduction, IUPAC nomenclature; Benzene; resonance, aromaticity; halogenation, Friedel Craft’s alkylation and acylation; chemical properties: mechanism of electrophilic substitution- Nitration sulphonation, directive influence of functional group in mono-substituted benzene; carcinogenicity and toxicity.
- Alkanes: Nomenclature, physical properties, structure of double bond (ethene), geometrical isomerism, methods of preparation: chemical reactions, addition of hydrogen, oxidation, ozonolysis, mechanism of electrophilic addition, halogen, water, hydrogen halides (Markovnikov’s addition and peroxide effect)
Read More
Detailed NEET Chemistry Syllabus of Class XII
Unit 1: Solutions
- Raoult’s law, depression of freezing point, elevation of boiling point, and osmotic pressure
- Van Hoff factor, Determination of molecular masses with the help of colligative properties abnormal molecular mass.
- Types of solutions, colligative properties- relative lowering of vapour pressure, solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids.
Unit 2: Solid State
- Calculation of density of unit cell, number of atoms per unit cell in a cubic unit cell, packing efficiency, voids, point defects, packing in solids, electrical and magnetic properties
- Band theory of metals, semiconductors and insulators
- Classification of solids based on different binding forces; amorphous and crystalline solids (elementary idea) conductors, molecular, ionic covalent and metallic solids,
- Unit cell in two and three dimensional lattices
Unit 3: Chemical Kinetics
- Rate of a reaction (average and instantaneous), temperature, concentration, factors affecting rates of reaction; catalyst; order and molecularity of a reaction
- Activation energy, Arrhenious equation
- Integrated rate equations and half life (only for zero and first order reactions);Rate law and specific rate constant, concept of collision theory ( elementary idea, no mathematical treatment)
Unit 4: Electrochemistry
- Kohlrausch’s Law, , dry cell- electrolytic cells, electrolysis, Laws of electrolysis (elementary idea), lead accumulator, Galvanic cells; EMF of a cell
- Relation between Gibbs energy change and EMF of a cell,Standard electrode potential, fuel cells; corrosion
- Conductance in electrolytic solutions, Redox reactions, specific and molar conductivity variation of conductivity with concentration
Unit 5: Processes of Isolation of Elements and General Principles
- Principles and methods of extraction- oxidation, oxidation, concentration,reduction electrolytic method
- Occurrence, copper, principles of extraction of aluminium, zinc and iron
Unit 6: Surface chemistry
- Adsorption– Physisorption and chemisorption; catalysis homogeneous and heterogeneous, activity and selectivity: factors affecting adsorption of gases on solids,enzyme catalysis
- Brownian movement, Tyndall effect, electrophoresis, coagulation; emulsions- types of emulsions
- Colloidal state:colloids and suspensions; distinction between true solutions, lyophobic multimolecular,lyophilic and macromolecular colloids
Unit 7: p- Block Elements
- Group-15 elements: Trends in physical and chemical properties; General introduction,occurrence, electronic configuration, oxidation states, compounds of phosphorus: preparation and properties of phosphine, halides (PCI3 , PCI5 ) and oxoacids (elementary idea only); oxides of nitrogen (structure only); Phosphorus- allotropic forms, preparation and properties of ammonia and nitric acid.
- Group-16 elements: Sulphur – allotropic forms; General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties; compounds of sulphur: preparation, properties and uses of sulphur dioxide; ozone. sulphuric acid: industrial process of manufacture, properties and uses, oxoacids of preparation, sulphur (structures only); dioxygen: preparation, properties and uses; classification of oxides; .
- Group-17 elements: Compounds of halogens: preparation,occurrence, electronic configuration, General introduction,oxidation states, properties and uses of chlorine and hydrochloric acid,trends in physical and chemical properties; interhalogen compounds oxoacids of halogens (structures only).
- Group-18 elements: electronic configuration, General introduction, trends in physical and chemical properties, occurrence, uses.
Unit 8: Coordination Compounds
- Coordination compounds: Introduction, coordination number, ligands,magnetic properties, colour, and shapes
- Importance of coordination compounds (in qualitative analysis as well as biological systems)
- Isomerism (structural and stereo) bonding, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds,Werner’s theory VBT,CFT
Unit 9: d and f Block Elements
- Lanthanide- oxidation states, electronic configuration, chemical reactivity, and lanthanoid contraction and its consequences.
- General introduction, characteristics of transition metals, electronic configuration, general trends in properties of the first row transition metals- metallic character, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii, colour, interstitial compounds, catalytic property, magnetic properties, alloy formation. Preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4.
- Actinoids: oxidation states,Electronic configuration, and comparison with lanthanide.
Unit 10: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Phenols: Nomenclature, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, methods of preparation, electrophilic substitution reactions, uses of phenols.
- Alcohols: Identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols; mechanism of dehydration, uses with special reference to methanol and ethanol; Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties (of primary alcohols only);.
- Ethers: Nomenclature, physical and chemical properties uses, methods of preparation, .
Unit 11: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Haloarenes: substitution reactions (directive influence of halogen for monosubstituted compounds Uses and environment effects of – dichloromethane,Nature of C-X bond, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, iodoform, freons, DDT only).
- Haloalkanes: Optical rotation, Nomenclature, nature of C –X bond, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of substitution reactions
Unit 12: Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Cyanides and Isocyanides: mentioned at relevant places.
- Amines: classification, structure, Nomenclature, methods of preparation, uses, identification of primary secondary amine, physical and chemical properties, and tertiary amine
- Diazonium salts: Chemical reactions, Preparation, and importance in synthetic organic chemistry.
Unit 13: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Carboxylic Acids: acidic nature, Nomenclature, physical and chemical properties; methods of preparation, uses.
- Aldehydes and Ketones: uses and Nomenclature, Mechanism of nucleophilic addition, nature of carbonyl group, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes; methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties.
Unit 14: Polymers
- Classification: Natural and synthetic, copolymerization, methods of polymerization (addition and condensation).
- Some important polymers: bakelite; natural and synthetic like polyesters, rubber, Biodegradable polymers, non-biodegradable polymers.
Unit 15: Biomolecules
- Proteins:peptide bond, Elementary idea of – amino acids, proteins, polypeptides, primary structure, secondary structure, denaturation of proteins; tertiary structure and quaternary structure (qualitative idea only), enzymes.
- Hormones: Elementary idea (excluding structure).
- Vitamins: Classification and function.
- Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA
- Carbohydrates: monosaccharide (glucose and fructose), Classification (aldoses and ketoses), polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen): importance, D.L. configuration, oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose),.
Unit 16: Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Chemicals in food: artificial sweetening agents, preservatives, elementary idea of antioxidants.
- Cleansing agents: soaps and detergents, cleansing action.
- Chemicals in medicines: tranquilizers,analgesics, antifertility drugs, antiseptics, disinfectants, antibiotics, antimicrobials,antihistamines, antacids.
NEET Syllabus 2021: Biology
Biology is no less important. However, the NEET 2021 syllabus Biology is quite concise. Specifically, it consists of both Zoology and Botany and there are a total of 10 chapters. For instance, the Biology section contains a total of 5 chapters from class XI and 5 from class XII. Following are these chapters:
| Chapters from Class XI | Chapters from Class XII |
| Diversity in Living World | Reproduction |
| Structural Organization in Animals and Plants | Genetics and Evolution |
| Cell Structure and Function | Biology and Human Welfare |
| Plant Physiology | Biotechnology and Its Applications |
| Human physiology | Ecology and environment |
Detailed NEET 2021 Syllabus Biology of Class XI
Unit 1: Cell Structure and Function
- Chemical constituents of living cells: Biomolecules-structure and function of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates; B Cell division: Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and their significance
- Golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles; mitochondria, ribosomes, plastids, microbodies; cilia, flagella, Cytoskeleton, centrioles (ultrastructure and function); Nucleus-nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleolus
- Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life; Cell envelope, cell membrane, cell wall; Cell organelles-structure and function; Plant cell and animal cell; Structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell; Endomembrane system-endoplasmic reticulum
Unit 2: Diversity in Living World
- What is living? Biodiversity; Need for classification; Taxonomy & Systematics; Three domains of life; Tools for study of Taxonomy – Museums, Zoos, Herbaria; Binomial nomenclature; Concept of species and taxonomic hierarchy
- Viruses and Viroids.
- Angiosperms- classification till class, characteristic features and examples). (Salient features with minimum two examples).
- Salient features and classification of animals – chordate up to classes level and non chordate up to phyla level
- Botanical gardens, Salient features and classification of plants into major groups- Gymnosperms, Algae, Pteridophytes, Bryophytes,
- Salient features and classification of Monera;
- Five kingdom classification; Lichens; Protista and Fungi into major groups
UNIT 3: Human Physiology
- Digestion and absorption;
- Alimentary canal and digestive glands;
- Role of digestive enzymes and gastrointestinal hormones;
- Peristalsis, digestion, absorption and assimilation of proteins, carbohydrates and fats;
- Caloric value of proteins, carbohydrates and fats;
- Egestion;
- Nutritional and digestive disorders – PEM, indigestion, constipation, vomiting, jaundice, diarrhoea
- Excretory Products and their elimination: Modes of excretion- Human excretory, ureotelism, Ammonotelism, uricotelism
- Body fluids and circulation: Composition of the blood, blood groups, coagulation of blood; Regulation of cardiac activity; Disorders of circulatory system-Hypertension, Coronary artery disease, Angina pectoris, Heart failure, Human circulatory system-Structure of Human heart and blood vessels; Composition of lymph and its function; Cardiac cycle, cardiac output, ECG, Double circulation
- Breathing and Respiration: Respiratory system in humans; Respiratory organs in animals (recall only); Mechanism of breathing and its regulation in humans-transport of gases, regulation of respiration and exchange of gases, Respiratory volumes; Disorders related to respiration-Occupational respiratory disorders, Asthma, Emphysema
- System – structure and function; Urine formation, Osmoregulation;
- Regulation of kidney function-Renin-angiotensin,
- Atrial Natriuretic Factor, ADH and Diabetes insipidus;
- Role of other organs in excretion; Disorders;
- Uraemia, Renal failure, renal calculi, Nephritis;
- Dialysis and artificial kidney
- Neural control and coordination: Neuron and nerves; Nervous system in humans- central nervous system, peripheral nervous system and visceral nervous system; Sense organs; Reflex action; Elementary structure and function of eye and ear; Generation and conduction of nerve impulse
- Locomotion and Movement: Types of movement- flagella, ciliary, muscular; skeletal system-Myasthenia and Disorders of muscular, Gravis, Muscular dystrophy, Tetany, Arthritis, Osteoporosis, Gout; Joints; Skeletal muscle- contractile proteins and muscle contraction; Skeletal system and its functions
- Pineal, Pancreas, Thyroid, Adrenal, Parathyroid, Gonads; Mechanism of hormone action (Elementary Idea); Role of hormones as messengers and regulators, Hypo-and hyperactivity and related disorders
- Chemical coordination and regulation: Endocrine glands and hormones; Human endocrine system-Hypothalamus, Pituitary
Click here for Chemistry Syllabus
UNIT 4: Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants
- Animal tissues; Morphology, anatomy and functions of different systems (respiratory, nervous, circulatory, digestive, and Syllabus) reproductive) of an insect (cockroach). (Brief account only)
- Morphology and modifications; Tissues; Anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants: Stem, Root, leaf, inflorescence- cymose and racemose, fruit, flower and seed
UNIT 5: Ecology and environment
- Ecosystem: Ecological Services – Carbon fixation, pollination, oxygen release, Energy flow; Patterns, components; productivity and decomposition; Nutrient cycling (carbon and phosphorous); Ecological succession; Pyramids of number, biomass, energy
- Organisms and environment: Population and ecological adaptations, Population interactions-mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism; Habitat and niche; Population attributes-growth, age distribution, and birth rate and death rate
- Environmental issues: Agrochemicals and their effects; Air pollution and its control; Radioactive waste management; Greenhouse effect and global warming; Solid waste management; Water pollution and its control; Ozone depletion; Deforestation;
- Any 3 case studies as success stories addressing environmental issues.
- Biodiversity and its conservation: Concept of Biodiversity, Biodiversity conservation, Importance of Biodiversity; Patterns of Biodiversity; Loss of Biodiversity; Hotspots, endangered organisms, biosphere reserves, extinction, National parks and sanctuaries, Red Data Book,
UNIT 6: Plant Physiology
- Elementary idea of Hydroponics as a method to study mineral nutrition;
- Nitrogen metabolism-biological, Nitrogen cycle, nitrogen fixation
- Transport in plants: Movement of water, Cell to cell transport-Diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport; gases and nutrients;
- Transpiration: Opening and closing of stomata
- Uptake and translocation of mineral nutrients: Mass flow hypothesis, Transport of food, phloem transport; Diffusion of gases (brief mention)
- Differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation; Sequence of developmental process in a plant cell; Growth regulators-auxin, gibberellin, ethylene, cytokinin, ABA; Seed dormancy; Photoperiodism, Vernalisation
- Plant – water relations – Imbibition, osmosis, water potential, plasmolysis; Long-distance transport of water – Absorption, Symplas, apoplast, transpiration pull, guttation and root pressure
- Photosynthesis: Factors affecting photosynthesis, Photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis; Site of photosynthesis take place; pigments involved in Photosynthesis (Elementary idea); Cyclic and non-cyclic and photophosphorylation; Chemiosmotic hypothesis; Photosynthesis as a means of Autotrophic nutrition; Photorespiration C3 and C4 pathways;
- Mineral nutrition: Essential minerals, Deficiency symptoms; Mineral toxicity; macro and micronutrients and their role
- Respiration: Exchange gases; Cellular respiration-glycolysis, fermentation (anaerobic), Energy relations-Number of ATP molecules generated; Amphibolic pathways; Respiratory quotient; TCA cycle and electron transport system (aerobic)
- Plant growth and development: Seed germination; Conditions of growth; Phases of Plant growth and plant growth rate
Check | NEET 2021 Preparation Tips for Biology
Detailed Class XII Syllabus of NEET Exam
Unit 1: Genetics and Evolution
- Molecular basis of Inheritance: Genome and human genome project; Structure of DNA and RNA; genetic code, translation; Gene expression and regulation-Lac Operon; Transcription, DNA fingerprinting, Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; DNA packaging; Central dogma; DNA replication.
- Heredity and variation: Co-dominance, Multiple alleles and Inheritance of blood groups, Pleiotropy; Elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; Mendelian Inheritance; Colour blindness; Linkage and crossing over; Sex linked inheritance-Haemophilia, Deviations from Mendelism-Incomplete dominance, Chromosome theory of inheritance, Chromosomes and genes; Sex determination-In humans, birds, honey bee, Mendelian disorders in humans-Thalassemia, Chromosomal disorders in humans; Down’s syndrome, Turner’s and Klinefelter’s syndromes.
- Evolution: Origin of life; Biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution from Paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidence); Hardy-Weinberg’s principle; Gene flow and genetic drift; Adaptive Radiation; Darwin’s contribution, Modern Synthetic theory of Evolution; Human evolution; Mechanism of evolution-Variation (Mutation and Recombination) and Natural Selection with examples, types of natural selection.
Unit 2: Reproduction
- Sexual reproduction in flowering plants: Flower structure; Development of male and female gametophytes; Double fertilization; Pollination Types, Post fertilization events- Development of endosperm and embryo, Development of seed and formation of fruit; agencies and examples; Outbreeding devices; Pollen-Pistil interaction; Special modes-apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed and fruit formation
- Reproductive health: Amniocentesis; Infertility and assisted reproductive technologies – IVF, ZIFT, GIFT (Elementary idea for general awareness); Birth control- Need and Methods, Need for reproductive health and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STD);Contraception and Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP).
- Reproduction in organisms: Modes-Binary fission, sporulation, budding, gemmule, fragmentation; vegetative propagation in plants; Reproduction, a characteristic feature of all organisms for continuation of species; Modes of reproduction – Asexual and sexual; Asexual reproduction.
- Human Reproduction: Gametogenesis- spermatogenesis & oogenesis; Pregnancy and placenta formation (Elementary idea); Parturition (Elementary idea); Male and female reproductive systems; Lactation (Elementary idea) Microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; Fertilisation, embryo development upto blastocyst formation, implantation; Menstrual cycle.
Unit 3: Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Principles and process of Biotechnology: Genetic engineering (Recombinant DNA technology), Modified organisms-Bt crops; Transgenic Animals; Biosafety issues-Biopiracy and patents.
- Human insulin and vaccine production, Application of Biotechnology in health and agriculture, gene therapy; Genetically
Unit 4: Biology and Human Welfare
- Microbes in human welfare: sewage treatment, energy generation, Industrial production, and as biocontrol agents and biofertilizers.
- Health and Disease; Typhoid, parasites causing human diseases (Malaria, Filariasis, Ascariasis. HIV and AIDS; Pneumonia, common cold, Cancer, amoebiasis, ringworm); Pathogens; Basic concepts of immunology-vaccines;Adolescence, drug and alcohol abuse.
- Improvement in food production; tissue culture, single cell protein, Biofortification; Plant breeding, Apiculture and Animal husbandry
Unit 5: Ecology and environment
- Ecosystem: Patterns, productivity and decomposition; Pyramids of number, components; biomass, energy; Nutrient cycling (carbon and phosphorous); Ecological succession; Ecological Services-Carbon fixation, Energy flow; pollination, oxygen release.
- Environmental issues: Air pollution and its control; Solid waste management; Radioactive waste management; Greenhouse effect and global warming; Water pollution and its control; Agrochemicals and their effects; Deforestation; Ozone depletion; Any three case studies along with the success stories to address environmental issues.
- Organisms and environment: Population interactions-mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism; Habitat and niche; Population attributes-growth,population and ecological adaptations; birth rate and death rate, age distribution
- Biodiversity and its conservation: Concept of Biodiversity; Biodiversity conservation; Patterns of Biodiversity; Hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red Data Book, biosphere reserves, National parks and sanctuaries; Importance of Biodiversity; Loss of Biodiversity.
Click here for Detailed Biology Syllabus
Topic wise weightage
The candidates should know about the section wise weightage in order to score high in NEET 2021 exam. Read the following content to identify the topic wise weightage.
NEET 2021 Physics Section Weightage
- It is assumed that Physics is more complicated compared to the other two subjects.
- Besides, the candidates usually spend more time in this section and the questions are time consuming.
- In the last year, there were eight difficult questions out of 45 questions in this section.
- Furthermore, Mechanics and Magnetism will be the two most important chapters and will carry the maximum weightage.
| Important Chapters | Weightage of Chapters in NEET 2021 |
| Mechanics | 10% |
| Thermodynamics | 9.5% |
| Current Electricity | 8.1% |
| Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation | 7.3% |
| Magnetism & Moving Charges | 6.3% |
| Kinematics | 6.0% |
| Rigid Body Dynamics | 5.6% |
| Work, Energy, and Power | 5.2% |
| Planar Motion | 4.4% |
| Ray Optics | 4.0% |
| Wave Optics | 3.3% |
| Kinetic Theory & Thermal Properties of Matter | 2.0% |
| Atomic Study | 1.3% |
| Waves | 1.0% |
| Gravitation | 1.0% |
Weightage of NEET 2021 Chemistry Section
- Chemistry is moderately difficult part in NEET 2021 Exam
- NEET 2021 Chemistry questions range from theoretical to reasoning based practical.
- The candidates should practice more the application based questions for NEET 2021
- Besides, based on the trend of previous years’ question papers, it can be assumed that more questions will come from class XII than class XI.
- For instance, 24 questions were coming from class XII and 21 questions from class XII in last year.
- Lastly, Physical chemistry and organic chemistry will carry the maximum weightage in the NEET 2021 exam.
Also check NEET 2021 Revision Plan
| Important Chapters | Weightage of Chapters in NEET 2021 |
| Chemical Bonding | 12.5% |
| Basic Concepts | 10.0% |
| Chemical Equilibrium | 8.2% |
| Carbonyl Compounds | 7.1% |
| Coordination Compounds | 6.7% |
| Organic Chemistry – II | 5.6% |
| Reaction Mechanism | 5.2% |
| The d and f Block Elements | 4.4% |
| IUPAC & Isomerism | 4.0% |
| Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry | 3.8% |
| Chemical Kinetics | 2.2% |
| Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | 2.2% |
| Chemistry in Everyday Life | 1.3% |
| Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | 1.0% |
| Environmental Chemistry | 0.8% |
Weightage of NEET 2021 Biology Section
- For instance, in the year 2017, there were 46 questions from class XII and 44 questions from class XI syllabus.
- This section is the easiest section compared to the rest. Hence, the candidates get scope to score high with the help of this section.
- As per prediction, most of the questions will come from Human Physiology and Plant Diversity in this year.
Check for more information, NEET Paper Analysis for identifying the chapters of each section that hold importance in the NEET 2021 syllabus weightage.
| Important Chapters | Weightage of Chapters in NEET 2021 |
| Human Physiology Biological Classification Molecular Basis of Inheritance | 12.0% |
| Biomolecules | 10.0% |
| Biological Classification | 9.0% |
| Molecular Basis of Inheritance | 8.2% |
| Animal Kingdom | 7.0% |
| Reproduction | 6.6% |
| Ecosystems | 5.1% |
| Human Health and Diseases | 4.3% |
| Biotechnology: Principles and Processes | 3.1% |
| Microbes in Human Welfare | 2.7% |
| Genetics | 2.1% |
| Plant Kingdom | 1.8% |
| Strategies for Enhancement of Food Production | 1.4% |
| Cell Biology | 1.0% |
| Plant Anatomy | 0.7% |
Best Books
Besides NCERT, the candidates should follow some subject specific NEET 2021 best books. Those books will be beneficial for them to clear their concept more. The chances of getting a high score will also be increased.
Best Books for Physics Preparation
| Book Name | Author Name |
| Concepts of Physics | H.C. Verma |
| Fundamentals of Physics | Halliday, Resnick and Walker |
| Objective Physics | D C Pandey |
| Complete NEET Guide | MTG Editorial Board |
Best Books for Chemistry Preparation
| Book Name | Author Name |
| Physical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry and Inorganic Chemistry | O.P. Tandon |
| Bull’s Eye Chemistry NEET Edition 2021 | Seema Saini and K.S. Saini |
| Organic Chemistry | Morrison and Boyd |
| MTG’s Objective NCERT at your fingertips | MTG Editorial Board |
Best Books for Biology Preparation
| Book Name | Author Name |
| Objective Biology (Volumes 1 & 2) | GR Bathla |
| Elementary Biology (Volume 1 & 2) | Trueman |
| A Class Book for Botany | A C Dutta |
| Complete NEET Guide: Biology | MTG Editorial Board |
The type of questions asked in National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET) are objective based type questions. The mode of the exam is offline. To prepare for the NEET 2021 exam, students should give first priority to those NCERT Class XI and XII books as they are most reliable. NCERT is written in simple language and is focused on concept-based teaching.
NEET 2021 Exam Pattern
Before appearing in the exam NEET 2021, the candidates should know the exam pattern including the marking scheme, total time duration and the other essential components. Hence, first read the following table to get to know about such important information:
| RESULT OF QUESTION | IMPACT |
| Popularly known as | NEET 2021 |
| Conducted by | NTA, MCI |
| Official website | ntaneet.nic.in |
| Number of questions | 180 |
| Type of questions | Multiple choice questions (MCQs) |
| Mode of examination | Offline (Pen and paper based) |
| Sections | Three (Physics, Chemistry and Biology) |
| Total score | 720 marks |
| Duration of exam | 3 hours |
| Negative marking | 180 |
To understand the exam pattern of NEET 2021 exam, the aspirants can take full length mock tests before the exam. Besides, they can also check NEET sample papers of previous years.
Marking Scheme of NEET 2021 Exam
- Each question of every paper carries 4 marks.
- Consequently, the candidates can acquire 4 marks for every correct answer.
- Besides, you will get 1 negative marking for every wrong answer.
- Nonetheless, If you do not attempt any question, you will not be negatively marked.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: The total number of question in NEET 2020 would be 180. 45 questions will be equally asked in all the sections, that is Physics, Chemistry, Botany and Zoology.
Ans: All the questions in NEET 2020 would be objective type, that is Multiple Choice Questions.
Ans: The Physics syllabus comprises of Class 11th and 12th syllabus:
- Class 11th: Physical world and measurement, Notion of Potential Entergy, Nature of Physical Laws, Kinematics, Speed, Velocity, Work, Energy and Power, Laws of Motion, Static & Kinetic Friction, Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body, Gravitation, Kepler’s law of Planetary Motion, The Universal Law of Gravitation, Thermodynamics, Behavior of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory, Properties of Bulk Matter, Bulk Modulus, Critical Velocity, Heat, Work & Internal Energy, Oscillations and Waves.
- Class 12th: Electrostatics, Electric Charges & their Conservation, Electric Dipole, Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism, Carbon Resistors, Kirchhoff’s Laws & Simple Applications, Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents, AC Generator & Transformer, Concept of Megnatic Field, Permanent Magnets, Current Electricity, Electromagnetic Waves, Electromagnetic Spectrum, Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation, Optics, Optical Instruments, Wave Optics, Atoms and Nuclei, Electronic Devices, Conductors
Ans: The Chemistry syllabus comprises of Class 11th and 12th syllabus as well. Below mentioned are all the topics:
- Class 11th : Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry, Laws of Chemical Combination, Structure of Atom, Atomic Number, Isotopes & Isobars, Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure, Ionic Bond, Covalent Bond, States of Matter: Gases and Liquids, Thermodynamics, Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties, Electronegativity, Equilibrium, Equilibrium in Physical & Chemical Process, Redox Reactions, Hydrogen, Physical & Chemical Properties of Water, s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline earth metals), Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles and Techniques, Some p-Block Elements, Hydrocarbons, Environmental Chemistry.
- Class 12th : Solid State, Band Theory of Metals, Solutions, Elevation of Boiling Point, Electro Chemistry, Chemical Kinetics, Surface Chemistry, General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements, Electrochemistry, p-Block Elements, d and f Block Elements, Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Alcohols, Physical & Chemical Properties of Primary Alcohol, Phenols and Ethers, Coordination Compounds, Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids, Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen, Amines, Cyanides & Isocyanides, Polymers, Biomolecules, Chemistry in Everyday Life, Cleansing Agents – Soaps & Detergents.
Ans: Biology syllabus comprises of questions from both Botany and Zoology. All the topics from which questions might be prompted in NEET 2020 are given below:
- Class 11th: Diversity in Living World, Three Domains of Life, Cell Structure and Function, Cell Theory, Plant Cell & Animal Cell, Structural Organization in Animals and Plants, Tissues, Morphology & Modifications, Plant Physiology, Transport in Plants, Photosynthesis, Human physiology.
- Class 12th: Reproduction, Reproduction in Organisms, Biology and Human Welfare, Genetics and Evolution, Heredity & Variations, Biology and Human Welfare, Biotechnology and Its Applications, Principle & Process of Biotechnology, Ecology and Environment, Organism & Environment, Biodiversity and its Conversation.
NEET 2021 Paper Analysis: Chapter Wise Weightage, Previous Year Paper Analysis
NEET 2021 was successfully conducted on 12 September 2021. Approximately 16 lakhs appeared for the NEET exam. Experts prepare the evaluation report and the aspirants can identify the difficulty level of the NEET question papers. Consequently, they can also predict the NEET cut off for the year. NEET paper analysis (2015 to 2021) has been highlighted in this article along with the difficulty level of the section wise topics.
NEET Physics Section was the toughest among all subjects while Biology section was the easiest. NEET 2021 Answer key will be released by the NTA in 4th week of september. As per the statement of experts, NEET cut off marks are dependent upon the difficulty level of the exam. It is advised to practice from NCERT books and previous years’ questions for NEET 2021 exam. Hence, the aspirants will get advantages to score high.
NEET 2021 Paper Analysis
NEET 2021 overall exam was moderate in terms of difficulty level.
| Subject | Difficulty Level |
| Physics | Difficult & Tricky |
| Chemistry | Easy |
| Biology | Easy |
NEET Physics Paper Analysis
- Physics section was the toughest and lengthy.
- 4-5 tricky questions were asked in both sections A & B.
- 70% of Physics paper was numerical based.
| Topics | Number of Questions |
| Electrodynamics | 20 |
| Mechanics | 15 |
| Heat | 2 |
| SHM Waves | 2 |
| Optics | 4 |
| Modern Physics and Electronics | 7 |
| Total | 50 |
NEET Chemistry Paper Analysis
- In comparison to the previous year paper, Chemistry section was difficult.
- Mostly questions were directlty asked from NCERT books.
- Approx 5 questions were matrix match type while 3 questions were graph based.
| Topics | Number of Questions |
| Physical Chemistry | 16 |
| Inorganic Chemistry | 17 |
| Organic Chemistry | 17 |
| Total | 50 |
NEET Biology Paper Analysis
- Botany section was easiest, while the Zoology section was slightly moderate in terms of difficulty level.
- Most questions in Botany section were directly asked from NCERT books.
- Few Zoology questions were tricky.
| Topics | Number of Questions |
| Biology in Human Welfare | 3 |
| Cell Structure & Functions | 9 |
| Diversity of Life | 5 |
| Ecology | 9 |
| Genetics | 11 |
| Plant Physiology | 8 |
| Reproduction and Sexual Reproduction | 4 |
| Structural organisation of Plants | 5 |
| Animal Husbandry & Biotechnology | 13 |
| Evolutions | 2 |
| Biomolecules | 5 |
| Human Health & Disease | 2 |
| Human Physiology | 10 |
| Human Reproduction & Reproductive Health | 6 |
| Structural Ogranisation in Plants | 4 |
| Animal Kingdom | 4 |
| Total | 100 |
NEET Paper Analysis 2020
NEET Paper analysis 2020 will paint a clear picture about the nature of the NEET 2021 exam to be conducted in future. This helps the future NEET aspirants to get prepared for the exam accordingly. Detailed analysis of all three sections are tabulated below:
NEET Physics Paper Analysis
- Physics again got the tag of the toughest section among the 3 sections.
- Direct questions from sections such as Energy, Mass, Newton’s Laws of Motion.
- Color code was asked from the current electricity question.
- Direct questions in this section were formula based.
| Section | Number of Questions |
| Mechanics | 16 |
| Heat and Thermodynamics | 5 |
| Electrostatics and Magnetism | 5 |
| Optics and Modern Physics | 10 |
| Current Electricity | 9 |
NEET Chemistry Paper Analysis
- Test takers found the Chemistry paper of NEET 2020 to be lengthier.
- Students found this section difficult, reason being lengthy calculations.
- Theoretical questions were a little difficult to solve.
- Overall this section ranked easy to solve and scoring also.
| Section | Number of Questions |
| Organic | 15 |
| Inorganic | 15 |
| Physical | 15 |
NEET Biology Paper Analysis
- Test takers perceive Biology questions very easy to solve.
- But some of the questions were tricky from this section.
- Most of the questions were straight from the NCERT syllabus.
| Section | Number of Questions |
| Biology in Human Welfare | 3 |
| Ecology | 11 |
| Plant Physiology | 7 |
| Human Physiology | 15 |
| Cell Structure | 6 |
| Structural organization in animal and plant | 7 |
| Biotechnology | 8 |
| Diversity of Living Organism | 12 |
| reproduction | 10 |
| Genetic and Evolution | 11 |
Overall Analysis of Questions in NEET 2020
| Particular | Physics | Chemistry | Biology |
| Number of questions from Class 11 | 22 | 21 | 52 |
| Number of questions from Class 12 | 23 | 24 | 38 |
| Overall Difficulty Level | Moderate-Difficult | Easy-Moderate | Easy-Moderate |
NEET Paper Analysis 2019
According to the applicants, the NEET 2019 question paper was moderately difficult. Some students found it lengthy. All three sections were a bit difficult. Physics section was a little bit tricky. The Chemistry section was also found moderately difficult. Biology section was easy compared to other sections but some of the questions were tough.
NEET 2019 Physics Paper Analysis
- Physics is the toughest section among the three sections in NEET 2019 exam.
- The aspirants will need to crack conceptually based and tricky questions in the exam.
- Physics questions were usually critical and the aspirants needed to do heavy calculations.
NEET 2019 Chemistry Paper Analysis
- Chemistry section was moderately complex. Hence, the aspirants got some direct questions from NCERT text book.
- This was the scoring section in NEET 2019 exam.
- As per the expert’s in depth NEET analysis, NEET 2019 chemistry was comparatively easier than the previous years.
NEET 2019 Biology Paper Analysis
- Usually, Biology is considered as the easiest section, however, last year, the Biology section was not so easy.
- The trend of NEET 2019 Biology questions was time-consuming and descriptive.
- The high weightage chapters of NEET 2019 biology section were from Microbes in Human Welfare and Cell. These are the chapters of Botany and Zoology respectively.
- To get a high score in the Biology section, the aspirants are required to have in-depth knowledge of concepts.
NEET 2019 Topic Wise Analysis (Physics & Chemistry)
| Topics | Easy | Average | Difficult | % Portion |
| Physics | ||||
| Mechanics | 3 | 4 | 2 | 22% |
| Fluids | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1% |
| Thermal Physics | 1 | 3 | 2 | 15% |
| SHM & Waves | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5% |
| Electrodynamics | 2 | 3 | 5 | 22% |
| Optics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 12% |
| Modern & Electronics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 16% |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Inorganic | 4 | 5 | 3 | 50% |
| Physical | 5 | 3 | 2 | 30% |
| Organic | 7 | 5 | 1 | 35% |
NEET 2019 Topic Wise Analysis (Biology)
Botany
| Topics | Easy | Medium | Difficult | Total |
| Plant Diversity | 2 | 5 | 1 | 8 |
| Ecology | 3 | 8 | 0 | 11 |
| Cell Biology and Cell division | 1 | 4 | 0 | 5 |
| Plant Morphology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Biomolecule | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Plant Physiology | 3 | 3 | 1 | 7 |
| Plant reproduction | 3 | 2 | 0 | 5 |
| Genetics & Biotechnology | 9 | 7 | 0 | 16 |
| Plant Anatomy | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| Total | 26 | 31 | 2 | 59 |
Zoology
| Topics | Easy | Medium | Difficult | Total |
| Animal Diversity | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| Structural Organisation in Animal | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Human Physiology | 8 | 6 | 1 | 15 |
| Human Reproduction and Reproductive health | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 |
| Origin and Evolution | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Human Health and Diseases | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Total | 19 | 8 | 4 | 31 |
NEET 2019 Paper Analysis by Allen Kota
According to Allen Kota’s experts, NEET 2019 paper ranked moderate to easy paper. Physics and Chemistry were easy according to Allen Kota analysis whereas the Biology paper of NEET 2019 UG exam, was somewhat lengthy. Below given table represents subject-wise difficulty level analysis by Allen Kota:
| Subject | No. of Easy Questions | No. of Medium Questions | No. of Difficult Questions |
| Physics | 21 | 21 | 3 |
| Chemistry | 27 | 13 | 5 |
| Botany | 32 | 17 | 1 |
| Zoology | 24 | 11 | 5 |
NEET 2019 Paper Analysis by Resonance
As per analysis by Resonance, the difficulty of Physics in NEET 2019 was higher than Chemistry and Biology. Among the total 45 multiple choice questions in Physics, 9 were difficult and tricky whereas Chemistry had only one very difficult question. The Biology section had a total of 17 difficult questions out of 90 multiple choice questions.
Overall NEET 2019 was found to be quite easier as compared to NEET 2018.The subject matter experts of Resonance said that questions from all subjects were found to be easier than the exam conducted in the last three years, therefore the cutoff should increase and is expected to be around 565 to 570.
Check NEET Syllabus 2021 Chemistry
NEET Paper Analysis 2018
Types of questions and the difficulty level of NEET 2018 exam were closely similar to NEET 2017. Both Physics and Chemistry gave a tough time to test takers due to long calculative questions. Few easy questions in Physics required tricky calculations. Biology was tough in comparison to previous years and was again time-consuming. It had few questions out of NCERT syllabus as well. Both Class XI and Class XII syllabus were covered in all the subjects. Check the in depth NEET analysis of 2018 as per the subjects below.
NEET Physics Paper Analysis
- In NEET 2018, Physics was the toughest section compared to the rest.
- Physics questions were comparatively lengthy and conceptual based.
- Category of Physics questions break up in NEET 2018 exam: 2 difficult questions, 34 easy questions and 9 moderate questions.
- In the NEET 2018 question paper, division of questions were 24 and 21 respectively from class XII and XI.
NEET Chemistry Paper analysis
- The Chemistry section was not so long like the Physics section.
- The section was moderate among the three sections.
- Most of the questions of the Chemistry section were simple concept based.
- The ratio of 12th standard and 11th standard questions were 20 and 20 respectively.
NEET Biology Paper analysis
- In NEET 2018, it was the easiest section compared to the other two sections.
- 46 questions were coming from class XII and 44 questions from class XI.
- There were 48 easy questions, 9 difficult questions and 33 moderate questions.
- Most of the questions were concept based and these were coming from NCERT (directly).
- Average obtained marks by most of the aspirants were ranking from 350 to 400 marks.
NEET 2018 Topic Wise Analysis (Physics, Chemistry & Biology)
| Topics | Easy | Average | Difficult | % Portion |
| Physics | ||||
| Mechanics | 5 | 7 | 0 | 27% |
| Fluids | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2% |
| Thermal Physics | 1 | 4 | 1 | 13% |
| SHM & Waves | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7% |
| Electrodynamics | 5 | 3 | 3 | 24% |
| Optics | 1 | 4 | 0 | 11% |
| Modern & Electronics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 16% |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Inorganic | 9 | 4 | 2 | 34% |
| Physical | 7 | 3 | 5 | 33% |
| Organic | 8 | 5 | 2 | 33% |
| Biology | ||||
| Plant Diversity | 6 | 1 | 0 | 11% |
| Plant Morphology | 4 | 3 | 0 | 11% |
| Plant Physiology | 1 | 4 | 1 | 10% |
| Plant Reproduction | 2 | 2 | 0 | 7% |
| Cell Biology | 3 | 5 | 1 | 15% |
Other Facts about NEET 2018
- Total number of applicants for NEET 2018 was 13, 26, 725. The ratio of male to female candidates is 580648: 746076. On the other hand, there was one transgender candidate as well.
- Since 2018, the exam has started to be conducted in other languages (irrespective of Hindi and English) such as Oriya, Urdu, Gujarati, Assamese, Kannada, Telugu, Tamil, Bengali, Marathi.
NEET Paper Analysis 2017
In terms of NEET difficulty level, experts and test takers rated NEET 2017 somewhere between ‘moderate to difficult’. Among the three sections, Physics continued to be the toughest while Biology and Chemistry were comparatively easier. Unexpectedly, a lot of questions were outside the NCERT syllabus which increased the difficulty level. In depth NEET Paper Analysis of 2017 for various sections is given below.
NEET Physics Paper Analysis
- In NEET 2017, most of the Physics questions had come from Class XI syllabus. Check NEET Syllabus 2021 Physics
- Most of the questions of Class XI were from Mechanics, Modern Physics and Electrodynamics of Class XI.
- There were 10 easy questions, 8 difficult questions and 27 moderate questions in NEET 2017.
- It was the toughest section similar to the other years.
NEET Chemistry Paper Analysis
- Unlike Physics, the aspirants had faced more questions in Chemistry from class XII.
- In NEET 2017, most of the questions were from Organic Chemistry. Nonetheless, inorganic chemistry carries the maximum weightage.
- The questions of class XI were very easy, whereas the questions of class XII were comparatively tricky.
- The students should have in-depth knowledge of the subject. Most of the Chemistry questions were conceptually based.
- The students should read the following chapters on top-notch priority:
- Chemical Bonding
- Coordination Compounds
- Carbonyl Compounds
- Organic Chemistry-I
Check and download the NEET Answer Key with Solution
NEET Biology Paper Analysis
- It was the easiest section for the students in NEET 2017 exam than Physics and Chemistry.
- This section was the saviour to the students.
- To get the idea about the NEET exam pattern and trend, the aspirants should follow the last 10 years Biology questions.
- However, it can be assumed that the biology exam will be tougher this year.
- Plant and human physiology were the most carrying topics of NEET 2017 Biology exam.
- In NEET 2017, 46 questions were coming from class XII and 44 were coming from class XI.
- Most of the questions of class XII were from the Zoology section and class XI were from Botany.
- The aspirants should read thoroughly the below mentioned chapters:
- Pollination
- Photosynthesis
- Endocrine System
- Digestive System
- Plant Anatomy
- DNA replication
- PAGE Theory
- Excretory and Nervous System
NEET 2017 Topic Wise Analysis (Physics, Chemistry & Biology)
| Topics | Easy | Average | Difficult | % Portion |
| Physics | ||||
| Mechanics | 3 | 4 | 7 | 31% |
| SHM & Waves | 2 | 1 | 0 | 7% |
| Heat & Thermodynamics | 4 | 1 | 1 | 13% |
| Properties of Matter | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4% |
| Electrodynamics | 3 | 4 | 2 | 20% |
| Modern Physics | 5 | 2 | 0 | 16% |
| Optics | 2 | 2 | 0 | 9% |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Inorganic | 7 | 6 | 2 | 33% |
| Physical | 7 | 5 | 5 | 31% |
| Organic | 4 | 8 | 4 | 36% |
| Biology | ||||
| The Living World | 1 | 6 | 2 | 10% |
| Structural Organization in Plant & Animal | 3 | 5 | 2 | 11% |
| Cell: Structure & Function | 1 | 4 | 3 | 9% |
| Plant Physiology | 1 | 5 | 2 | 9% |
| Animal Physiology & Reproduction | 9 | 8 | 4 | 21% |
| Reproduction in Plants | 5 | 9 | 5 | 6% |
| Genetics & Evolution | 0 | 3 | 2 | 12% |
| Biology in human welfare | 2 | 2 | 1 | 6% |
| Biotechnology | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3% |
| Ecology | 5 | 3 | 4 | 13% |
Check NEET Syllabus 2021 Biology
NEET Paper Analysis 2016
The NEET 2016 exam pattern remained almost the same. For instance, the questions for each section were distributed almost equally between class XI and XII syllabus. Physics section was tougher and time consuming in comparison to the other sections. Biology section was easier and Chemistry was rated average. You can find NEET Paper Analysis for 2016 divided into sections below:
NEET 2016 Topic Wise Analysis (Physics, Chemistry & Biology)
| Topics | Easy | Average | Difficult | % Portion |
| Physics | ||||
| Mechanics | 6 | 4 | 1 | 24% |
| SHM & Waves | 2 | 2 | 1 | 9% |
| Heat & Thermodynamics | 1 | 4 | 0 | 11% |
| Properties of Matter | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4% |
| Electrodynamics | 3 | 6 | 2 | 24% |
| Modern Physics | 2 | 4 | 2 | 18% |
| Optics | 1 | 3 | 0 | 9% |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Inorganic | 4 | 7 | 2 | 28% |
| Physical | 4 | 9 | 3 | 36% |
| Organic | 3 | 9 | 4 | 36% |
| Biology | ||||
| The Living World | 6 | 8 | 1 | 17% |
| Structural Organization in Plant & Animal | 5 | 4 | 1 | 11% |
| Cell: Structure & Function | 4 | 1 | 2 | 8% |
| Plant Physiology | 5 | 1 | 1 | 8% |
| Animal Physiology & Reproduction | 9 | 8 | 4 | 23% |
| Reproduction in Plants | 4 | 1 | 0 | 6% |
| Genetics & Evolution | 3 | 2 | 2 | 8% |
| Biology in human welfare | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3% |
| Biotechnology | 3 | 2 | 0 | 6% |
| Ecology | 6 | 4 | 0 | 11% |
Check | How to Prepare for NEET Without Coaching?
NEET Paper Analysis 2015
NEET 2015 was the first time CBSE conducted entrance exam. It was popular as a single window entrance examination across India. In terms of overall difficulty, the experts and candidates rated it average. Biology was difficult while Physics and Chemistry paper was comparatively easier. The paper also had a few questions beyond NCERT syllabus. Given below is NEET Paper Analysis according to sections.
NEET 2015 Topic Wise Analysis (Physics, Chemistry & Biology)
| Topics | Easy | Average | Difficult | % Portion |
| Physics | ||||
| Mechanics | 8 | 2 | 1 | 24% |
| SHM & Waves | 2 | 1 | 0 | 7% |
| Heat & Thermodynamics | 5 | 1 | 0 | 13% |
| Properties of Matter | 2 | 0 | 0 | 5% |
| Electrodynamics | 4 | 4 | 3 | 24% |
| Modern Physics | 6 | 2 | 1 | 20% |
| Optics | 2 | 1 | 0 | 7% |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Inorganic | 5 | 6 | 5 | 36% |
| Physical | 5 | 6 | 5 | 36% |
| Organic | 5 | 6 | 2 | 28% |
| Biology | ||||
| The Living World | 2 | 7 | 2 | 12% |
| Structural Organization in Plant & Animal | 2 | 5 | 1 | 9% |
| Cell: Structure & Function | 2 | 9 | 0 | 12% |
| Plant Physiology | 0 | 5 | 2 | 9% |
| Animal Physiology & Reproduction | 4 | 12 | 2 | 20% |
| Reproduction in Plants | 0 | 3 | 0 | 14% |
| Genetics & Evolution | 0 | 10 | 3 | 14% |
| Biology in human welfare | 0 | 5 | 0 | 6% |
| Biotechnology | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2% |
| Ecology | 2 | 8 | 2 | 13% |
Check and download NTA NEET 2021 Sample Papers
Takeaway from Previous Years Sample Paper Analysis
It is clearly visible that a few topics have a high weightage each year. You need to work on these topics thoroughly. There is also a chance that the Biology section might have a high number of questions from Zoology instead of Botany. Your aim should be to prepare major topics for both the subjects. To score good marks in NEET 2021, you can read more about NTA NEET 2021 preparation tips and follow the schedule for NEET Preparation 2021.
NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus: Important Chapters, Topics and Best Books to refer
NTA has published NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus on its official website. Physics section carries 25% weightage out of 180 total marks of NEET 2021 exam. To check the NEET 2021 syllabus, you have to visit nta neet.nic.in.
Since NEET (UG) is now the only examination for admission in medical institutes in India, hence, the difficulty level might reduce. But to secure admission in a top-tier medical course, you have to solve NEET previous years question papers and sample papers with utmost dedication. It will also help you to understand the weightage of the questions of each section.
3 subjects are assessed in the examination – Physics, Chemistry, Biology. NCERT books of class 11th and 12th for each subject are extremely important while preparing for NEET 2021. Specifically, NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus is considered to be the toughest among the three subjects.
So, what should be the first step to start your NEET 2021 preparation? To begin with, aspirants should know the syllabus of each subject. Even though the NEET 2021 syllabus has not been announced this year, it is expected to be same as 2020.
Read: Why NCERT Books are Important for NEET 2021 Exam?
NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus – Overview
NEET 2021 Physics syllabus is directly taken from what students study in their Class 11 and 12 NCERT textbooks. NEET Physics syllabus given below is always recommended.
| NEET Physics Syllabus for Class 11 | NEET Physics Syllabus for Class 12 |
| Physics World and Measurement | Electrostatics |
| Kinematics | Current Electricity |
| Laws of Motion | Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism |
| Work, Energy and Power | Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents |
| Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body | Electromagnetic Waves |
| Gravitation | Optics |
| Properties of Bulk Matter | Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation |
| Thermodynamics | Atoms and Nuclei |
| Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory | Electronic Devices |
| Oscillation and Waves | – |
Check | NEET 2021 Preparation Tips for Physics
NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus: Class XI
UNIT I: Physical World and Measurement
- Physics: Physics, technology, and society; Nature of physical laws; Scope and excitement.
- Need for measurement: Units of measurement; SI units, fundamental and derived units; systems of units. Length, mass and time measurements; errors in measurement; significant figures; accuracy and precision of measuring instruments.
- Dimensions of physical quantities, its application and dimensional analysis.
UNIT II: Kinematics
- Motion in a straight line, Frame of reference; Uniformly accelerated motion, velocity-time and position-time graphs, for uniformly accelerated motion (graphical treatment). Position-time graph, speed and velocity. Non – uniform and uniform motion, instantaneous velocity and average speed.
- Elementary concepts of integration and differentiation for describing motion. Scalar and vector quantities: Displacement and position vectors, general vectors, general vectors and notation, equality of vectors, multiplication of vectors by a real number; addition and subtraction of vectors. Relative velocity.
- Unit vectors. Resolution of a vector in plane-rectangular components.
- Scalar and Vector products of Vectors. Motion in a plane. Cases of uniform acceleration and uniform velocity – projectile motion. Uniform circular motion.
UNIT III: Laws Of Motion
- Inertia, Intuitive concept of force, Newton’s first law of motion, momentum and Newton’s second law of motion, impulse, Newton’s third law of motion, Law of conservation of linear momentum and its applications.
- Static and Kinetic friction, Lubrication, laws of friction, rolling friction.
- Equilibrium of concurrent forces,
- Dynamics of uniform circular motion,
- Centripetal force, examples of circular motion (vehicle on level circular and banked road).
UNIT IV: Work, Energy, and Power
- Work done by a constant and variable force, work-energy theorem, kinetic energy, power.
- Notion of potential energy, potential energy of a spring, conservative forces; conservation of mechanical energy (kinetic and potential energies), non-conservative forces, motion in a vertical circle, elastic and inelastic collisions in one and two dimensions.
UNIT V: Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body
- Centre of the mass of the rigid body, centre of mass of the uniform rod.
- Centre of the mass of the two-particle system, momentum conservation and centre of mass motion.
- Moment of a force, angular momentum, conservation of angular momentum with some examples, -torque.
- Equilibrium of rigid bodies, comparison of linear and rotational motions, rigid body rotation and equation of rotational motion, the moment of inertia, radius of gyration.
- Values of M.I. for simple geometrical objects (no derivation).
- Statement of perpendicular and parallel and axes theorems and their applications.
UNIT VI: Gravitation
- Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. Acceleration due to gravity and its variation with depth and altitude. The universal law of gravitation.
- Gravitational potential energy, gravitational potential.
- Escape velocity, orbital velocity of a satellite.
- Geostationary satellites.
UNIT VII: Properties of Bulk Matter
- Elastic behavior, Stress-strain relationship.
- Poisson’s ratio, elastic energy.
- Young’s modulus, bulk modulus, shear, modulus of rigidity, Hooke’s law.
- Stokes’ law, Viscosity, terminal velocity, streamline and turbulent flow, Reynold’s number.
- Critical velocity, Bernoulli’s theorem and its applications.
- Surface energy and surface tension, application of surface tension ideas to drops, angle of contact, excess of pressure, bubbles and capillary rise.
- Temperature, heat, thermal expansion, thermal expansion of solids, liquids, and gases.
- Specific heat capacity: Cp, change of state-latent heat, Cv-calorimetry.
- Anomalous expansion.
- Heat transfer-conduction and thermal conductivity, radiation and convection.
- Qualitative ideas of Wein’s displacement law, Black Body Radiation, and GreenHouse effect.
- Stefan’s Law and Newton’s law of cooling.
UNIT VIII: Thermodynamics
- Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: Thermal equilibrium and definition of temperature.
- First law of thermodynamics.
- Heat, work and internal energy.
- Isothermal and adiabatic processes.
- Second law of the thermodynamics: Reversible and irreversible processes. Heat refrigerators and engines.
UNIT IX: Behavior of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory
- Work done on compressing a gas, equation of state of a perfect gas.
- Kinetic theory of gases: Assumptions, concept of pressure. Kinetic energy and temperature, law of equipartition of energy (statement only), degree of freedom and application to specific heat capacities of gases, concept of mean free path, concept of gases.
UNIT X: Oscillations and Waves
- Periodic motion-period, displacement as a function of time, frequency.
- Periodic functions.
- Simple harmonic motion (SHM) and its equation.
- Phase, simple pendulum – derivation of expression for its time period, forced, energy in SHM –Kinetic and potential energies, oscillations of a spring-restoring force and force constant, free and damped oscillations ( qualitative ideas only), resonance.
- Wave motion. Displacement relation for a progressive wave.
- Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of wave motion. Reflection of waves, standing waves in strings and organ pipes, the principle of superposition of waves, fundamental mode and harmonics.
Beats. - Doppler Effect.
NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus: Class XII
UNIT I: Electrostatics
- Electric charges and their conservation.
- Coulomb’s law-force between two point charges, superposition principle and continuous charge distribution, forces between multiple charges, .
- Electric field, electric field due to a point charge, electric dipole, electric field lines, torque on a dipole in a uniform electric field, electric field due to a dipole.
- Statement of Gauss’s theorem and its applications to find field due to infinitely long straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell( field inside and outside), Electric flux.
- Electric potential, electric potential due to a point charge, potential difference, a dipole and system of charges: equipotential surfaces, electrical potential energy of a system of two point charges and of electric dipoles in an electrostatic field.
- Conductors and insulators, bound charges inside a conductor and free charges.
- Dielectrics and electric polarization, combination of capacitors in series and in parallel, capacitors and capacitance, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates, Van de Graff generator, energy stored in a capacitor.
UNIT II: Current Electricity
- Electric current, drift velocity and mobility, and their relation with electric current, flow of electric charges in a metallic conductor, electrical resistance, Ohm’s law, V-I characteristics (linear and nonlinear), electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical energy and power.
- Carbon resistors, series and parallel combinations of resistors, color code for carbon resistors, temperature dependence of resistance.
- Internal resistance of a cell, potential difference and emf of a cell, combination of cells in parallel and in series.
- Kirchhoff’s laws and simple applications. metre bridge and Wheatstone bridge.
- Potentiometer-principle and applications to measure potential difference, measurement of internal resistance of a cell, comparing emf of two cells.
UNIT III: Magnetic Effects Of Current And Magnetism
- Concept of magnetic field, Oersted’s experiment.
- Biot Savart law and its application to current carrying circular loops.
- Ampere’s law and its applications to infinitely long straight wire, straight and toroidal solenoids.
- Cyclotron, Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields.
- Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field.
- Force between two parallel current-carrying conductors-definition of ampere.
- Torque experienced by a current loop in a magnetic field, moving coil galvanometer-its current sensitivity and conversion to voltmeter and ammeter.
- Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment, Magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron.
- Magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole along its axis and perpendicular to its axis.
- Torque on a magnetic dipole in a uniform magnetic field, magnetic field lines, bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid, Earth’s magnetic field and magnetic elements.
- Paramagnetic, ferro-megnatic and dia- magnetic substances, with examples.
- Permanent magnets, Electromagnetic and factors affecting their strengths.
UNIT IV: Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
- Electromagnetic induction, induced emf and current, Faraday’s law, Eddy currents, Lenz’s law.
- Mutual and self inductance.
- Alternating currents, peak and rms value of alternating current/voltage, reactance and impedance, LCR series circuit, resonance, power in AC circuits, wattless current, LC oscillations (qualitative treatment only).
- AC generator and transformer.
UNIT V: Electromagnetic Waves
- Need for displacement current
- Electromagnetic waves and its characteristics.
- Transverse nature of electromagnetic waves.
- Electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves, infrared, microwaves, ultraviolet, visible, gamma rays, x-rays) including elementary facts about their uses.
Read More
UNIT VI: Optics
- Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror formula.
- Reflection of light, total internal reflection and its applications optical fibres, refraction at spherical surfaces, lenses, thin lens formula, lens-maker’s formula.
- Magnification, combination of thin lenses in contact combination of a lens and a mirror, power of a lens.
- Dispersion and Refraction of light through a prism.
- Scattering of light-blue colour of the sky and reddish appearance of the sun at sunset and sunrise.
- Optical instruments: Human eye, correction of eye defects (hypermetropia and myopia) using lenses, image formation and accommodation.
- Microscopes and astronomical telescopes (refracting and reflecting) and their magnifying powers.
- Proof of laws of refraction and reflection using Huygens’ principle.
- Wave optics: Wavefront and Huygens’ principle, refraction and reflection of plane waves at a plane surface using wavefronts.
- Interference, coherent sources and sustained interference of light, Young’s double hole experiment and expression for fringe width.
- Diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maximum.
- Polarization, Brewster’s law, uses of plane polarized light and Polaroids, plane polarized light.
- Resolving power of microscopes and astronomical telescopes.
UNIT VII: Dual Nature Of Matter And Radiation
- Hertz and Lenard’s observations, Photoelectric effect, Einstein’s photoelectric equation-particle nature of light.
- De Broglie relation, matter waves – wave nature of particles.
- Davisson-Germer experiment.
UNIT VIII: Atoms And Nuclei
- Rutherford’s model of atom, Alpha-particle scattering experiments, Bohr model, energy levels, hydrogen spectrum.
- Composition and size of nucleus, isotopes, isobars, isotones, atomic masses.
- Radioactivity- alpha, gamma and beta rays/particles and their properties decay law.
- Mass-energy relation, binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number, mass defect, nuclear fusion and fission.
UNIT IX: Electronic Devices
- Energy bands in solids (qualitative ideas only), insulators, conductors, and semiconductor diode- I-V characteristics in reverse and forward bias, I-V characteristics of LED, diode as a rectifier, photodiode, , Zener diode as a voltage regulator, solar cell, and Zener diode.
- Junction transistor, characteristics of a transistor, transistor action, transistor as an amplifier and oscillator.
- Logic gates (OR, NOT, NOT, NOR and NAND), Transistor as a switch.
The whole NEET 2021 Physics syllabus PDF is downloadable and you can refer to the official document provided by NTA here. Or students can print this page using Ctrl+P and keep this as a reminder of the long list of topics they have to prepare for!
Check| Detailed NEET 2021 Syllabus of Chemistry
Weightage of Important Topics in NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus
Some topics of NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus are more important than others as they are repeatedly asked in the NEET previous year question papers. Some of the important topics of NEET Physics Syllabus are mentioned in the table below-
| NEET Physics Important Chapters | Weightage in NEET Physics Syllabus |
| Laws of Motion | 15% |
| System of Particle and Rigid Body | 14% |
| Thermodynamics | 14% |
| Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetism | 12% |
| Current Electricity | 13% |
| Semiconductor Electronics | 12% |
| Atoms and Nuclei | 10% |
| Ray Optics and Optical Instrument | 10% |
Read More
Most Important Chapters of NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus
Physics syllabus for NEET is vast, and you cannot skip any major topic. Specifically, the NEET previous year question papers for Physics had about 19 questions from the class XI syllabus and around 26 questions from class XII syllabus. Therefore, it is essential to cover all the chapters that are mentioned in the official NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus.
Also Check NEET 2021 Revision Plan.
Very Important Topics of NEET Physics Syllabus
| Electronic Devices |
| Electrostatics |
| Heat and Thermodynamics |
| Kinematics |
| Laws of Motion |
| Magnetic effect of Current and Magnetism |
| Oscillations and Waves |
Moderately Important Topics of NEET Physics Syllabus
| Atoms and Nuclei |
| Current Electricity |
| Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation |
| Electromagnetic Induction |
| Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body |
| Optics |
| Work, Energy & Power |
Less Important Topics of NEET Physics Syllabus
| Alternating Current |
| Behavior of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory |
| Electromagnetic Waves |
| Gravitation |
| Physical World and Measurement |
| Properties of Bulk Matter |
The major point to be noted is that the questions were mostly from the topics covered in the NCERT books based on the analysis of the last year question paper. Here the important topics of NEET Physics syllabus from which the questions are mostly asked in exam-
Number of Questions Expected from Various Topics
| Topics of Physics Syllabus for NEET 2021 | No of Questions Expected |
| Mechanics | 19 |
| Electrodynamics | 9 |
| Modern Physics | 7 |
| Optics and Wave Optics | 5 |
| Thermodynamics | 5 |
Chapter-wise difficulty in NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus
Given below is an analysis of difficulty of questions bifurcated chapter-wise. As the table below suggests, NEET Physics Syllabus requires deep knowledge of each topic. Specifically, the number of easy questions has completely vanished in the past few years. Considerably, almost all the questions in NEET Physics are moderate or tough. Furthermore, the major getaway from this is that due to a higher difficulty level, competition in NEET is saturated towards the top 10% to 20% of the candidates only.
| Unit | Number of Questions | Easy | Moderate | Difficult |
| Mechanics | 17 | 0 | 16 | 1 |
| Heat and Thermodynamics | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Properties of matter | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Electrostatics and Capacitor | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Current Electricity | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Magnetism, Magnetic Effect of Current and AC | 5 | 0 | 4 | 1 |
| Modern Physics | 6 | 0 | 5 | 1 |
| Ray and Way Optics | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Total | 45 | 0 | 41 | 4 |
NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus: Preparation Tips
NEET Physics syllabus is considered as difficult due to confusing patterns and also because it includes a wide range of scientific principles and numerical problems. Again, the top experts will not deny this fact. Hence, you should clear your concept first. Afterward, to cover the whole syllabus from 0 to 100, the students should follow a strategy.
Some Useful NEET 2021 Preparation Tips for Physics Syllabus
- Know NEET 2021 syllabus and exam pattern – Learn about what is going to be asked in the examinations. Check NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus and keep a print out of it as a task list accordingly. On the other hand, NEET 2021 Exam Pattern helps you to understand the intricacies of the exam.
- Focus on important concepts – The most important topics of NEET Physics Syllabus are – Mechanics, Heat, and Thermodynamics, Electrodynamics and also Modern Physics. This is based on past year trends. For instance, almost 50-60% of paper is set on these topics.
- Remember all formulae – Learning a formula is easy. However, learning a whole book of formulae is pretty difficult. Therefore, students must maintain a short book for these and keep revising the most important formulae accordingly.
- Practice old question papers – During the last few weeks of preparation, it is necessary to work on all the topics with equal importance. Therefore, take a pen and paper and solve the maximum old question papers.
- Create short notes – You must make notes of all the essential formulae, theorems and also principles when you are learning the topics for the first time. Consequently, this will help you during revision as short notes help in a quick go-through.
- Practice with Online Mock Tests – Take as many NEET mock tests as possible. Therefore, this will help you score well due to higher practice and also make you adapt to a computer-based environment. Moreover, mock analysis are available from each attempted test which will also help you to understand the weak topics
- Work on weak topics – Prioritize on most important topics of NEET Physics Syllabus and then plan for the less important ones. Moreover, working on mock will help in knowing the weak areas. Additionally, various websites provide topic-based tests to practice on various difficulty levels.
Check NEET 2021 Preparation Tips
Best Books for NEET 2021 Preparation of Physics Syllabus
We have listed some important books to prepare aspirants for a strong base in NEET 2021 Physics syllabus subsequently. However, remember that this list is not exhaustive. You can refer to other books too if you find them useful.
| Book | Author |
| Physics for Medical Entrance Examinations | D.C. Pandey |
| Concepts of Physics | H.C. Verma |
| Fundamentals of Physics | Halliday, Resnick and Walker |
| Objective NCERT at your fingertips for NEET AIIMS- Physics | MTG Editorial Board |
| Complete NEET Guide | MTG Editorial Board |
| NEET 2020 Physics Guide- 5th Edition | Disha Publications |
According to a large number of medical aspirants and experts, Physics is comparatively more tricky and conceptual based. Hence, this is the reason why most of the candidates find the NEET Physics questions toughest than the other two sections. For example, the NEET 2021 appearing candidates are advised to practice questions with the low to heavy calculations to improve their performance in the examination.
NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus – Check Detailed Syllabus and Important Topics
NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus is very vast and can be classified into three parts, namely- Physical, Organic and Inorganic Chemistry. NEET 2021 covers Chemistry Syllabus as prescribed in CBSE class XI and class XII NCERT books. The students have to answer 45 questions in the NTA NEET 2021 Chemistry section. Check NEET 2021 Exam pattern.
NTA has not published an official notice related to changes in NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus. So it is pretty clear that the NTA NEET 2021 Chemistry syllabus would be similar to NEET Syllabus 2020.
The best NEET 2021 preparation tips for Chemistry Syllabus is to prepare the top 10 important topics of NEET Chemistry Syllabus thoroughly along with that you can start devising your self-study plan. The more time you allot to the high weightage chapters higher will be your score in NTA NEET 2021 chemistry section. Not to forget, the more the revision, the better is the performance. Check NEET 2021 Revision Plan.
NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus– Chapters
Find the following table to identify the important topics of NEET Chemistry Syllabus:
| Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Laws of Chemical Combination |
| Structure of Atom, Atomic Number | Isotopes & Isobars |
| Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Ionic Bond |
| Covalent Bond | States of Matter: Gases and Liquids |
| Thermodynamics | Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties |
| Electronegativity | Equilibrium |
| Equilibrium in Physical & Chemical Process | Redox Reactions |
| Hydrogen | Physical & Chemical Properties of Water |
| S-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline earth metals) | Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles and Techniques |
| Some p-Block Elements | Hydrocarbons |
| Environmental Chemistry | Solid State |
| Band Theory of Metals | Solutions |
| Elevation of Boiling Point | Chemical Kinetics |
| Surface Chemistry | General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements |
| Electrochemistry | p-Block Elements |
| d and f Block Elements | Haloalkanes and Haloarenes |
| Alcohols | Physical & Chemical Properties of Primary Alcohol |
| Phenols and Ethers | Coordination Compound |
| Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen |
| Amines, Cyanides & Isocyanides | Polymers |
| Biomolecules | Chemistry in Everyday Life |
| Cleansing Agents – Soaps & Detergents | – |
Click here for NEET 2021 Syllabus of Biology
Detailed Class 11th NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus
Given below is the detailed NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus from Class 11th. The syllabus can be saved using Ctrl + P (Print) option to download the NEET Chemistry Syllabus PDF.
UNIT I: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Atomic and molecular masses
- Laws of chemical combination, Dalton’s atomic theory: concept of elements, atoms and molecules
- General Introduction: Important and scope of chemistry
- Mole concept and molar mass; percentage composition and empirical and molecular formula; chemical reactions, stoichiometry and calculations based on stoichiometry
UNIT II: Structure of Atom
- Atomic number, isotopes and isobars. Concept of shells and subshells, dual nature of matter and light, de Broglie’s relationship, Heisenberg uncertainty principle, concept of orbital, quantum numbers, shapes of s,p and d orbitals, rules for filling electrons in orbitals- Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principles and Hund’s rule, electronic configuration of atoms, stability of half filled and completely filled orbitals.
UNIT III: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Modern periodic law and long form of periodic table, periodic trends in properties of elements- atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, electronegativity, valence.
UNIT IV: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Valence electrons, ionic bond, covalent bond, bond parameters, Lewis structure, polar character of covalent bond, valence bond theory, resonance, geometry of molecules, VSEPR theory, concept of hybridization involving s, p and d orbitals and shapes of some simple molecules, molecular orbital theory of homonuclear diatomic molecules (qualitative idea only). Hydrogen bond.
UNIT V: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids
- Three states of matter, inter molecular interactions, types of bonding, melting and boiling points, role of gas laws of elucidating the concept of the molecule, Boyle’s law, Charle’s law, Gay Lussac’s law, Avogadro’s law, ideal behavior of gases, empirical derivation of gas equation.
- Avogadro number, ideal gas equation. Kinetic energy and molecular speeds (elementary idea), deviation from ideal behavior, liquefaction of gases, critical temperature. Liquid State- Vapour pressure, viscosity and surface tension (qualitative idea only, no mathematical derivations).
UNIT VI: Thermodynamics
- First law of thermodynamics-internal energy and enthalpy, heat capacity and specific heat, measurement of U and H, Hess’s law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of: bond dissociation, combustion, formation, atomization, sublimation, phase transition, ionization, solution and dilution
- Introduction of entropy as state function, Second law of thermodynamics, Gibbs energy change for spontaneous and non-spontaneous process, criteria for equilibrium and spontaneity
- Third law of thermodynamics- Brief introduction
UNIT VII: Equilibrium
- Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes, dynamic nature of equilibrium, law of chemical equilibrium, equilibrium constant, factors affecting equilibrium-Le Chatelier’s principle; ionic equilibrium- ionization of acids and bases, strong and weak electrolytes, degree of ionization, ionization of polybasic acids, acid strength, concept of PH., Hydrolysis of salts (elementary idea), buffer solutions, Henderson equation, solubility product, common ion effect (with illustrative examples)
UNIT VIII: Redox Reactions
- Concept of oxidation and oxidation and reduction, redox reactions oxidation number, balancing redox reactions in terms of loss and gain of electron and change in oxidation numbers
UNIT IX: Hydrogen
- Occurrence, isotopes, preparation, properties and uses of hydrogen; hydrides-ionic, covalent and interstitial; physical and chemical properties of water, heavy water; hydrogen peroxide-preparation, reactions, uses and structure
UNIT X: s-Block Elements (Alkali and Alkaline earth metals)
- General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, anomalous properties of the first element of each group
- Group I and group 2 elements: diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties (such as ionization enthalpy, atomic and ionic radii), trends in Sodium carbonate, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide and sodium hydrogen carbonate, biological importance of sodium
- Preparation and Properties of Some important Compounds: chemical reactivity with oxygen, water, hydrogen and halogens; uses. Industrial use of lime and limestone, biological importance of Mg and Ca and potassium
UNIT XI: Some p-Block Elements
- General Introduction to p-Block Elements
- Group 13 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, variation of properties, oxidation states, trends in chemical reactivity, anomalous properties of the first element of the group; Boron, some important compounds: borax, boric acids, boron hydrides. Aluminium: uses, reactions with acids and alkalis
- General 14 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, variation of properties, oxidation states, trends in chemical reactivity, anomalous behavior of the first element. Carbon, allotropic forms, physical and chemical properties: uses of some important compounds: oxides
- Important compounds of silicon and a few uses: silicon tetrachloride, silicones, silicates and zeolites, their uses
UNIT XII: Organic Chemistry- Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- General introduction, methods of purification, qualitative and quantitative analysis, classification and IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds.
- Electronic displacements in a covalent bond: inductive effect, electromeric effect, resonance and hyperconjugation
- Homolytic and heterolytic fission of a covalent bond: free radials, carbocations, carbanions; electrophiles and nucleophiles, types of organic reactions.
UNIT XIII: Hydrocarbons
- Alkanes: Nomenclature, isomerism, conformations (ethane only), physical properties, chemical reactions including free radical mechanism of halogenation, combustion and pyrolysis.
- Alkanes: Nomenclature, structure of double bond (ethene), geometrical isomerism, physical properties, methods of preparation: chemical reactions: addition of hydrogen, halogen, water, hydrogen halides (Markovnikov’s addition and peroxide effect), ozonolysis, oxidation, mechanism of electrophilic addition.
- Alkynes: Nomenclature, structure of triple bond (ethyne), physical properties, methods of preparation, chemical reactions: acidic character of alkynes, addition reaction of- hydrogen, halogens, hydrogen halides and water.
- Aromatic hydrocarbons: Introduction, IUPAC nomenclature; Benzene; resonance, aromaticity; chemical properties: mechanism of electrophilic substitution- Nitration sulphonation, halogenation, Friedel Crafts alkylation and acylation; directive influence of functional group in mono-substituted benzene; carcinogenicity and toxicity.
UNIT XIV: Environmental Chemistry
- Environmental pollution: Air, water and soil pollution, chemical reactions in atmosphere, smogs, major atmospheric pollutants; acid rain ozone and its reactions, effects of depletion of ozone layer, greenhouse effect and global warming- pollution due to industrial wastes; green chemistry as an alternative tool for reducing pollution, strategy for control of environmental pollution
Click here for NEET 2021 Syllabus of Physics
Detailed Class 12th NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus
UNIT I: Solid State
- Classification of solids based on different binding forces; molecular, ionic covalent and metallic solids, amorphous and crystalline solids (elementary idea), unit cell in two dimensional and three-dimensional lattices, calculation of density of unit cell, packing in solids, packing efficiency, voids, number of atoms per unit cell in a cubic unit cell, point defects, electrical and magnetic properties, Band theory of metals, conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
UNIT II: Solutions
- Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids, solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, colligative properties- relative lowering of vapour pressure, Raoult’s law, elevation of boiling point, depression of freezing point, osmotic pressure, determination of molecular masses using colligative properties abnormal molecular mass. Van’t Hoff factor.
UNIT III: Electrochemistry
- Redox reactions, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar conductivity variation of conductivity with concentration, kohlrausch’s Law, electrolysis and Laws of electrolysis (elementary idea), dry cell- electrolytic cells and Galvanic cells; lead accumulator, EMF of a cell, standard electrode potential, Relation between Gibbs energy change and EMF of a cell, fuel cells; corrosion.
UNIT IV: Chemical Kinetics
- Rate of a reaction (average and instantaneous), factors affecting rates of reaction; concentration, temperature, catalyst; order and molecularity of a reaction; rate law and specific rate constant, integrated rate equations and half life (only for zero and first order reactions); concept of collision theory ( elementary idea, no mathematical treatment). Activation energy, Arrhenious equation.
UNIT V: Surface chemistry
- Adsorption– Physisorption and chemisorption; factors affecting adsorption of gases on solids, catalysis homogeneous and heterogeneous, activity and selectivity: enzyme catalysis; colloidal state: distinction between true solutions, colloids and suspensions; lyophilic, lyophobic multimolecular and macromolecular colloids; properties of colloids; Tyndall effect, Brownian movement, electrophoresis, coagulation; emulsions- types of emulsions.
UNIT VI: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Principles and methods of extraction- concentration, oxidation, reduction electrolytic method and refining; occurrence and principles of extraction of aluminium, copper, zinc and iron.
UNIT VII: p- Block Elements
- Group 15 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, oxidation states, trends in physical and chemical properties; preparation and properties of ammonia and nitric acid, oxides of nitrogen (structure only); Phosphorus- allotropic forms; compounds of phosphorus: preparation and properties of phosphine, halides (PCI3 , PCI5 ) and oxoacids (elementary idea only).
- Group 16 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties; dioxygen: preparation, properties and uses; classification of oxides; ozone. Sulphur – allotropic forms; compounds of sulphur: preparation, preparation, properties and uses of sulphur dioxide; sulphuric acid: industrial process of manufacture, properties and uses, oxoacids of sulphur (structures only).
- Group 17 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties; compounds of halogens: preparation, properties and uses of chlorine and hydrochloric acid, interhalogen compounds oxoacids of halogens (structures only).
- Group 18 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties, uses.
UNIT VIII: d and f Block Elements
- General introduction, electronic configuration, characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first row transition metals- metallic character, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii, colour, catalytic property, magnetic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy formation. Preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4.
- Lanthanoids- electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical reactivity, and lanthanoid contraction and its consequences.
- Actinoids: Electronic configuration, oxidation states and comparison with lanthanide.
UNIT IX: Coordination Compounds
- Coordination compounds: Introduction, ligands, coordination number, colour, magnetic properties and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds, isomerism (structural and stereo) bonding, Werner’s theory VBT,CFT; importance of coordination compounds (in qualitative analysis, biological systems)
UNIT X: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Haloalkanes: Nomenclature, nature of C –X bond, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of substitution reactions, Optical rotation.
- Haloarenes: Nature of C-X bond, substitution reactions (directive influence of halogen for monosubstituted compounds Uses and environment effects of – dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, iodoform, freons, DDT only).
UNIT XI: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Alcohols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties (of primary alcohols only); identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols; mechanism of dehydration, uses with special reference to methanol and ethanol.
- Phenols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophilic substitution reactions, uses of phenols.
- Ethers: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties uses.
UNIT XII: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Aldehydes and Ketones: Nomenclature, nature of carbonyl group, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; and mechanism of nucleophilic addition, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes; uses.
- Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; uses.
UNIT XIII: Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses,identification of primary secondary and tertiary amine
- Cyanides and Isocyanides: will be mentioned at relevant places.
- Diazonium salts: Preparation, chemical reactions and importance in synthetic organic chemistry.
UNIT XIV: Biomolecules
- Carbohydrates: Classification (aldoses and ketoses), monosaccharide (glucose and fructose), D.L. configuration, oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen): importance.
- Proteins: Elementary idea of – amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides, proteins, primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure and quaternary structure (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins; enzymes.
- Hormones: Elementary idea (excluding structure).
- Vitamins: Classification and function.
- Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA
UNIT XV: Polymers
- Classification: Natural and synthetic, methods of polymerization (addition and condensation), copolymerization. Some important polymers: natural and synthetic like polyesters, bakelite; rubber, Biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers.
UNIT XVI: Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Chemicals in medicines: analgesics, tranquilizers, antiseptics, disinfectants, antimicrobials, antifertility drugs, antibiotics, antacids, antihistamines.
- Chemicals in food: preservatives, artificial sweetening agents, elementary idea of antioxidants.
- Cleansing agents: soaps and detergents, cleansing action.
Check Official NTA NEET 2021 Syllabus for Physics, Chemistry and Biology
Most Important Topics of NEET Chemistry Syllabus
As stated before, NEET Chemistry Syllabus comes under 3 sub-sections – Physical, Organic and Inorganic Chemistry. All of these three sections have almost equal weightage. But it is also important to note that in each of these 3 sections, there are certain chapters which have much higher weightage and are thus very important. Nevertheless, candidates must give importance to every topic in the NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus. Some topics were asked repeatedly in NEET Previous Year Question Papers. Candidates can check the table mentioned below to understand the NEET 2021 Syllabus Weightage of Chemistry-
| Important Topics of NEET Chemistry Syllabus | Weightage (in percentage) |
| Mole Concept and General Physical Chemistry | 8% |
| Chemical bonding and molecular structure | 7% |
| Carbonyl Compounds – Aldehydes, Carboxylic Acids | 7% |
| Coordination compounds | 6% |
| p-Block elements | 6% |
| s-Block elements and Hydrogen | 6% |
| Chemical Equilibrium | 6% |
| Chemical Thermodynamics | 6% |
| Biomolecules and Polymers | 5% |
| Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers | 4% |
| Chemical Kinetics | 4% |
Read: Why NCERT books are important for NEET 2021 Preparation?
Weightage for NEET Chemistry Syllabus: Inorganic
| Topics | Questions | Total Marks |
| P and S block | 2 | 8 |
| Chemical Bonding | 5 | 20 |
| Periodic Table | 1 | 4 |
| D and F block | 2 | 8 |
| Coordination Compounds | 4 | 16 |
| Qualitative Analysis | 1 | 4 |
| Metallurgy | 1 | 4 |
| Total | 16 | 64 |
Weightage for NEET Physical Chemistry
| Topics | Questions | Total Marks |
| Chemical Equilibrium | 3 | 12 |
| Nuclear Chemistry and Atomic Structure | 1 | 4 |
| Thermochemistry and Thermodynamics | 2 | 8 |
| Mole Concept | 1 | 4 |
| Electrochemistry | 1 | 4 |
| Chemical Kinetics | 2 | 8 |
| Solution and Colligative Properties | 1 | 4 |
| Solid State | 1 | 4 |
| Surface Chemistry | 1 | 4 |
| Total | 13 | 52 |
Read More
Weightage for NEET Chemistry Syllabus: Organic
| Topics | Questions | Total Marks |
| Alkyl Halide, Alcohol and Ether | 2 | 8 |
| General Organic Chemistry | 3 | 12 |
| Biomolecules | 1 | 4 |
| Aromatic Compounds | 1 | 4 |
| Chemistry in Everyday Life | 1 | 4 |
| Carbonyl Compounds | 4 | 16 |
| IUPAC & Isomerism | 2 | 8 |
| Environmental Chemistry | 1 | 4 |
| Practical Organic Chemistry | 1 | 4 |
| Total | 16 | 64 |
NEET 2021 Preparation Tips For Chemistry
NEET questions are generally simple. Although the NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus is wide and has too much to study, the questions are repetitive and with a simple twist. Practicing regularly with NEET Previous Year Question Papers will help improve the performance by a large margin. Additionally, the candidates need to be quick and wise in the selection of questions to clear the exam with a good score.
Also Check | NEET 2021 Sample Papers
Given below are some tips to improvise the learning of NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus-
Best NEET 2021 Preparation Tips for Chemistry Syllabus
- Solve, Learn and Practice: The key to success in the NEET 2021 chemistry section is practicing maximum questions. Solve the questions on your own at first attempt, learn from the mistakes and practice more of such questions.
- Practice Papers and Mock Tests: It is important to attempt maximum NEET mock tests or practice papers for NEET. Watch video lectures over how to attempt the NEET 2021 Chemistry section the right way and learn the strategy of toppers.
- Inorganic chemistry must be learned throughout the year: As inorganic chemistry has a vast syllabus and difficult structural diagrams, best to practice them regularly.
- NCERT is your X-Factor: NEET questions are mostly asked directly from specific lines of a specific chapter, so try to by heart the concepts with line.
- Reference books: Along with NCERT books candidates must refer some other books that give you space for practice.
- Last day preparation: Make a small pocket manual for yourself where you can keep all the important concepts handy, or a collection of information that can be used for studying the important topics of NEET Chemistry Syllabus at the last minute.
- Never try new things in the last few days: As the NEET 2021 Syllabus of Chemistry is quite vast. This requires you to follow a timetable and study things with some gaps and space, but do not learn anything new in the last few days, if you have not worked with it previously.
- Last minute revision: Revision is an important part of the syllabus, so just revise everything you have learned in the last few days.
- Take care of your health: Best to eat small meals at regular intervals to keep your mind fresh. Take proper sleep of at least 6 hours!
Check Complete NEET 2021 Preparation Tips
NTA Video Lectures For NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus
On the official portal of NTA, students can find video lectures by IIT-PAL which are watchable on mobile phones or tablets as well. The videos are uploaded on the IIT-PAL page on Youtube. There are more than 100 video lectures of about 50 to 60 minutes duration for each video. Lectures are divided according to topics of various chapters and are prepared by reputed faculty members of top IITs. To access these videos-
- Go to www.nta.ac.in
- Click on ‘Students’ tab
- Select Content Based Lectures under ‘Test Practice’ section
- Select Chemistry video lectures.
- New page on youtube will load showing a playlist of lectures.
Free NEET Mock Tests by NTA for NEET Chemistry Syllabus
NTA also provides free mock tests on the official portal. Students can head over to – www.nta.ac.in/quiz to access the Mock Tests. These mock tests can be attempted on a computer free of cost and also do not require any registration on the website. The papers given in these mock tests are of previous years of NEET examination. Section-wise mocks are available here so a student can focus on questions from NEET Chemistry Syllabus. It is advised to attempt the mocks once the whole syllabus is completed.
Best Books for NEET Chemistry Syllabus
Identify the best books for NEET Chemistry Syllabus suiting your study style and work with them at regular intervals, so that you are able to master the NEET Chemistry Syllabus in the due course of time.
MCQs for NEET Chemistry are generally not very difficult, except with a few exceptions. Students must stick to the best time management of work in order to perform best within the stipulated time period. Some good books for NEET Chemistry syllabus are as follows:
| Book name | Publisher | ISBN |
| A to Z Chemistry for NEET Class XI | Cengage Learning India Pvt Ltd | 8131534200 |
| Universal Self-Scorer Errorless Chemistry (Set of 2 Volumes) | Universal Books Depot | 8193000218 |
| Marvel Chemistry MCQs Volume 2 For NEET(UG) And JEE (Main) Exams | Marvel Publication | 8193371747 |
| Objective Chemistry – Chapter-wise MCQ for JEE Main/ BITSAT/ AIPMT/ AIIMS/ KCET 2nd Edition | Disha Publications | 9385576712 |
As stated all over this article, NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus is vast but not exactly difficult. Only the student should keep practicing consistently and with full dedication. It is important to stick with the NEET Chemistry Syllabus and the NEET 2021 exam pattern. Keep in mind that there is negative marking for every incorrect answer in NEET and OMRs do not have any option to change the answer!
NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus- Detailed Syllabus and Preparation Tips
NEET Biology section carries 50% score of total 180 questions in NEET 2021 exam. The entire Biology section is classified into two subsections and these are Zoology and Botany. Both these subsections carry 50% weightage. Furthermore, NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus by NTA comprises the NCERT prescribed topics.
- Thorough practice and consistency are the two best possible ways to get a good score in the Biology section.
- If prepared well with a good time management plan, you can score up to 90% in the biology section.
- Many of you are not big fans of the plant kingdom unit, as there are plenty of scientific terms that are used in this unit. So the best option is to prepare this at last as the percentage weightage of this unit is only 1% to 3%.
You can be free from the hassles of technical preparations and rote learning if you just follow the article closely. This article will turn out to be a complete NEET Guide for Biology.
Also Read:
NEET Biology Syllabus Highlights
| Total weightage of NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus | 50% of NEET score |
| Subsection | Botany and Zoology |
| Number of questions asked | 90 |
| Marks allotted for each question | +4 marks for a correct answer |
| Negative marking | -1 mark for the wrong answer |
| Total marks for Biology | 360 out of 720 marks |
NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus of Class 11th and 12th
| NEET 2021 Biology syllabus of Class 11th | Weightage |
| Unit I – Diversity in Living World | 9% |
| Unit II- Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants | 9% |
| Unit III- Cell Structure and Function | 15% |
| Unit IV- Plant Physiology | 17% |
| Unit V- Human physiology | 28% |
| NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus Class 12th | Weightage |
| Unit I – Reproduction | 14% |
| Unit II – Genetics and Evolution | 7% |
| Unit III – Biology and Human Welfare | 18% |
| Unit IV – Biotechnology and its Applications | 12% |
| Unit V – Ecology and Environment | 19% |
Also Read | Top Medical Colleges of India
NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus – Chapters
NTA NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus is subdivided into two sections that are Zoology and Botany. 45 questions are asked from each section, which means the NEET Biology section will be asking a total of 90 questions. Remember there are a total of 180 questions to be solved in just 180 minutes. To maximize the score in the NEET Biology section, candidates must give priority to both sub-sections. As per the notice by NTA, NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus is almost similar to that of NEET 2020 Biology Syllabus.
Given below are the chapters from NTA NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus:
- Diversity in Living World
- Structural Organization in Animals and Plants
- Cell Structure and Function
- Plant Physiology
- Human Physiology
- Reproduction
- Genetics and Evolution
- Biology and Human Welfare
- Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Ecology and Environment
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Also Check NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus
Detailed NEET Biology Syllabus of Class XI
UNIT I: Diversity in Living World
- What is living? Biodiversity; Need for classification; Three domains of life; Taxonomy & Systematics; Concept of species and taxonomic hierarchy; Binomial nomenclature; Tools for study of Taxonomy – Museums, Zoos, Herbaria
- Five kingdom classification, salient features and classification of Monera; Protista and Fungi into major groups; Lichens;
- Botanical gardens, Salient features and classification of plants into major groups-Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms
- Viruses and Viroids, Salient features and classification of animals: nonchordate up to phyla level and chordate up to classes level (three to five Angiosperms (three to five salient and distinguishing features and at least two examples of each category) Angiosperms- classification up to class, characteristic features and examples), Salient features and at least two examples).
UNIT II: Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants
- Morphology and modifications; Tissues; Anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants: Root, stem, leaf, inflorescence- cymose and racemose, flower, fruit and seed (To be dealt along with the relevant practical of the Practical)
- Animal tissues; Morphology, anatomy and functions of different systems (digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and Syllabus) reproductive) of an insect (cockroach). (Brief account only)
UNIT III: Cell Structure and Function
- Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life, cell wall, Structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell, Cell envelope, Plant cell and animal cell, cell membrane, Cell organelles-structure and function; Endomembrane system-endoplasmic reticulum,
- Golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles; mitochondria, ribosomes, plastids, microbodies; Cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, centrioles (ultrastructure and function); Nucleus-nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleolus
- Chemical constituents of living cells: Biomolecules-structure and function of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids; B Cell division: Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and their significance
Must Read NEET 2021 Sample Papers
UNIT IV: Plant Physiology
- Transport in plants: Movement of water, gases and nutrients; Cell to cell transport-Diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport;
- Plant – water relations – Imbibition, water potential, osmosis, plasmolysis; Long-distance transport of water – Absorption, apoplast, symplast, transpiration pull, root pressure and guttation;
- Transpiration: Opening and closing of stomata
- Uptake and translocation of mineral nutrients: Transport of food, phloem transport, Mass flow hypothesis; Diffusion of gases (brief mention)
- Mineral nutrition: Essential minerals, macro and micronutrients and their role; Deficiency symptoms; Mineral toxicity;
- Elementary idea of Hydroponics as a method to study mineral nutrition; Nitrogen metabolism-Nitrogen cycle, biological, nitrogen fixation
- Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis as a means of Autotrophic nutrition; Site of photosynthesis take place; pigments involved in Photosynthesis (Elementary idea); Photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis; Cyclic and non-cyclic and photophosphorylation; Chemiosmotic hypothesis; Photorespiration C3 and C4 pathways; Factors affecting photosynthesis
- Respiration: Exchange gases; Cellular respiration-glycolysis, fermentation (anaerobic), TCA cycle and electron transport system (aerobic); Energy relations-Number of ATP molecules generated; Amphibolic pathways; Respiratory quotient.
- Plant growth and development: Seed germination; Phases of Plant growth and plant growth rate; Conditions of growth
- Differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation; Sequence of developmental process in a plant cell; Growth regulators-auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene, ABA; Seed dormancy; Vernalisation; Photoperiodism
UNIT V: Human Physiology
- Digestion and absorption; Alimentary canal, digestive glands; Role of digestive enzymes, gastrointestinal hormones; Peristalsis, digestion, absorption and assimilation of proteins, carbohydrates and fats; Caloric value of proteins, carbohydrates and fats; Egestion; Nutritional and digestive disorders – PEM, indigestion, constipation, vomiting, jaundice, diarrhea
- Breathing and Respiration: Respiratory organs in animals (recall only); Respiratory system in humans; Mechanism of breathing and its regulation in humans-Exchange of gases, transport of gases and regulation of respiration Respiratory volumes; Disorders related to respiration-Asthma, Emphysema, Occupational respiratory disorders
- Body fluids and circulation: Composition of the blood, blood groups, coagulation of blood; Composition of lymph and its function; Human circulatory system-Structure of human heart and blood vessels; Cardiac cycle, ECG, Double circulation; Regulation of cardiac activity; Disorders of circulatory system-Hypertension, Coronary artery disease, Angina pectoris, Heart failure.
- Excretory Products and their elimination: Modes of excretion- Ammonotelism, ureotelism, uricotelism; Human excretory
- System-structure and function; Urine formation, Osmoregulation; Regulation of kidney function-Renin-angiotensin, Atrial Natriuretic Factor, ADH and Diabetes insipidus; Role of other organs in excretion; Disorders; Uraemia, Renal failure, renal calculi, Nephritis; Dialysis and artificial kidney
- Locomotion and Movement: ciliary, flagellar, muscular movements; Skeletal muscle- contractile proteins and muscle contraction; Skeletal system and its functions; Joints; Disorders of muscular and skeletal system-Myasthenia Gravis, Tetany, Muscular dystrophy, Arthritis, Osteoporosis, Gout.
- Neural control and coordination: Neuron and nerves; Nervous system in humans- central nervous system, peripheral nervous system and visceral nervous system; Generation and conduction of nerve impulse; Reflex action; Sense organs; Elementary structure and function of eye and ear.
- Chemical coordination and regulation: Endocrine glands and hormones; Human endocrine system-Hypothalamus, Pituitary,
- Pineal, Thyroid, Parathyroid, Adrenal, Pancreas, Gonads; Mechanism of hormone action (Elementary Idea); Role of hormones as messengers and regulators, Hypo-and hyperactivity and related disorders.
Also Check NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus
Read More
Detailed NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus of Class XII
UNIT I: Reproduction
- Reproduction in organisms: Reproduction, a characteristic feature of all organisms for continuation of species; Modes of reproduction – Asexual and sexual; Asexual reproduction; Modes-Binary fission, sporulation, budding, gemmule, fragmentation; vegetative propagation in plants
- Sexual reproduction in flowering plants: Flower structure; Development of male and female gametophytes; Pollination Types, agencies and examples; Outbreeding devices; Pollen-Pistil interaction; Double fertilization; Post fertilization events- Development of endosperm and embryo, Development of seed and formation of fruit; Special modes-apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed and fruit formation
- Human Reproduction: Male and female reproductive systems; Microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; Gametogenesis- spermatogenesis & oogenesis; Menstrual cycle; Fertilisation, embryo development up to blastocyst formation, implantation; Pregnancy and placenta formation (Elementary idea); Parturition (Elementary idea); Lactation (Elementary idea).
- Reproductive health: Need for reproductive health and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STD); Birth control- Need and Methods, Contraception and Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP); Amniocentesis; Infertility and assisted reproductive technologies – IVF, ZIFT, GIFT (Elementary idea for general awareness).
UNIT II: Genetics and Evolution
- Heredity and variation: Mendelian Inheritance; Deviations from Mendelism-Incomplete dominance, Co-dominance, Multiple alleles and Inheritance of blood groups, Pleiotropy; Elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; Chromosome theory of inheritance; Chromosomes and genes; Sex determination-In humans, birds, honey bee; Linkage and crossing over; Sex-linked inheritance-Haemophilia, Colour blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans-Thalassemia; Chromosomal disorders in humans; Down’s syndrome, Turner’s and Klinefelter’s syndromes.
- Molecular basis of Inheritance: Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; Structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; DNA replication; Central dogma; Transcription, genetic code, translation; Gene expression and regulation-Lac Operon; Genome and human genome project; DNA fingerprinting.
- Evolution: Origin of life; Biological evolution and evidence for biological evolution from Paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidence); Darwin’s contribution, Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution; Mechanism of evolution-Variation (Mutation and Recombination) and Natural Selection with examples, types of natural selection; Gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy-Weinberg’s principle; Adaptive Radiation; Human evolution
UNIT III: Biology and Human Welfare
- Health and Disease; Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (Malaria, Filariasis, Ascariasis. Typhoid, Pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ringworm); Basic concepts of immunology-vaccines; Cancer, HIV and AIDS; Adolescence, drug and alcohol abuse.
- Improvement in food production; Plant breeding, tissue culture, single-cell protein, Biofortification; Apiculture and Animal husbandry
- Microbes in human welfare: In household food processing, industrial production, sewage treatment, energy generation and as biocontrol agents and biofertilizers.
UNIT IV: Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Application of Biotechnology in health and agriculture: Human insulin and vaccine production, gene therapy; Genetically
- Principles and process of Biotechnology: Genetic engineering (Recombinant DNA technology), modified organisms-Bt crops; Transgenic Animals; Biosafety issues-Biopiracy and patents.
UNIT V: Ecology and environment
- Organisms and environment: Habitat and niche, Population and ecological adaptations, Population interactions-mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism, Population attributes-growth, birth rate and death rate, age distribution
- Ecosystem: Patterns, components; productivity and decomposition; Energy flow; Pyramids of number, biomass, energy; Nutrient cycling (carbon and phosphorous); Ecological succession; Ecological Services-Carbon fixation, pollination, oxygen release.
- Biodiversity and its conservation: Concept of Biodiversity; Patterns of Biodiversity; Importance of Biodiversity; Loss of Biodiversity; Biodiversity conservation; Hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red Data Book, biosphere reserves, National parks and sanctuaries.
- Environmental issues: Air pollution and its control; Water pollution and its control; Agrochemicals and their effects; Solid waste management; Radioactive waste management; Greenhouse effect and global warming; Ozone depletion; Deforestation; Any three case studies as success stories addressing environmental issues.
Read Complete NEET 2021 Syllabus
NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus: Topic-wise Weightage
While students start preparing for the whole syllabus, they forget what requires more attention. A lot of coaching institutes and school teachers focus on topics which are cumulatively important for the board exams but do not reveal their weightage in NEET examination. A chapter which has more than 4% weightage in NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus can be considered important as 4% constitutes about 3 to 4 questions out of 180 or about 14 to 15 marks out of 720. This means that the chances of a question being asked from that particular chapter are much more. Given below is a table which specifies the weightage of all the topics of NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus:
| Biology Syllabus for NEET | Weightage (%) |
| Human Physiology Biological Classification Molecular Basis of Inheritance | 12.0% |
| Biomolecules | 10.0% |
| Biological Classification | 9.0% |
| Molecular Basis of Inheritance | 8.2% |
| Animal Kingdom | 7.0% |
| Reproduction | 6.6% |
| Ecosystems | 5.1% |
| Human Health and Diseases | 4.3% |
| Biotechnology: Principles and Processes | 3.1% |
| Microbes in Human Welfare | 2.7% |
| Genetics | 2.1% |
| Plant Kingdom | 1.8% |
| Strategies for Enhancement of Food Production | 1.4% |
| Cell Biology | 1% |
| Plant Anatomy | 0.7% |
Read: Why NCERT books are important for NEET 2021 Preparation?
NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus: Difficulty Analysis
NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus by NTA constitutes 50% of the weightage for NEET overall. Considering the importance of the exam, the high weightage seems reasonable. According to the past analysis of various sessions of NEET, the trend seems to be like this-
- Around 50% of the questions from the Biology section are Easy.
- 30% to 35% Questions are Moderate in terms of difficulty.
- 15% to 20% Questions are Difficult to answer for everyone.
| Section | Easy Questions | Moderate Questions | Difficult Questions |
| Botany | 21 | 17 | 7 |
| Zoology | 20 | 19 | 6 |
A good score in NEET Biology is said to be around 200 to 300 marks. If a student has good speed and knowledge here, NEET Biology score can easily reach above 200.
NEET 2021 Preparation Tips for Biology Syllabus
- Try and relate to the definition of scientific terms, instead of mugging them
- Discuss the terms and definitions learned with your friends, this will help you in remembering the definitions better
- Sketch a diagram daily related to the syllabus defined, as plenty of questions are related to diagrams
- Most biology questions are from NCERT books, practice well
- Keep a metric check of your score in various NEET important topics, that will help you in identifying the weak topics
- Do regular practices of MCQs from different topics
- Try to work with the 10-year papers and NEET mock tests
- Do a self-check of the answers, go for comparative study
- Track of your performance by keeping a graph of your score in various test series.
NTA Free Video Lectures for NEET Biology Syllabus (IIT-PAL)
Aspirants who are weak in any particular topic of NEET Biology Syllabus can cover these topics easily by watching video lectures from top subject experts. The video lectures are uploaded under the nemesis of IIT-PAL on Youtube.
The video lectures are available under playlists made for various topics of Class XI and XII with lectures duration ranging from 45 minutes to 1 hour for a single topic. To access these lectures follow the steps below:
- Go to the official website of NTA – nta.ac.in
- Click on the ‘Students’ tab.
- Click on ‘Content Based Lectures’ under Test Practice Center.
- Once the new page loads, click on Biology which will direct you to the Youtube Page.
- Alternatively, students can also search for IIT-PAL Biology lectures on Youtube on their mobile phone or tablet.
NEET Previous Year Question Papers
If a student is unable to find the right source for NEET Previous Year Question Papers, he/she can always refer to the NTA Website which also provides old question papers of almost every examination.
To download NEET Previous Year Question Papers-
- Head over to www.nta.ac.in
- Click on the ‘Downloads’ tab
- Now, in this new page, look for Previous Year Question Papers
- Choose the year and the exam as NEET.
- List of available papers will be populated.
- Click on Download Link to save the PDF of question papers.
NTA Free Mock Tests for NEET Biology Syllabus
NTA has provided free mock tests for NEET Biology as well as other subjects from NEET. Aspirants can attempt these mocks at the comfort of their homes. A stable internet connection will be required along with a compatible browser such as Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge. The NTA mock tests are available section-wise which helps students focus on a particular topic.
To access NEET mock tests, follow steps below-
- Head to – www.nta.ac.in
- Click on the ‘Students’ tab
- Select Mock Test under Test Practice section.
- Now choose the exam you are appearing for and select the section you wish to attempt.
- Start the NEET mock test.
Check Complete NEET 2021 Preparation Tips
Best Books For NEET Biology Syllabus
In order to get an edge in your final performance in the exam, you must work with some best books for NEET Biology Syllabus. There are books that must be referred to specific topics and books that can be used as MCQ reference manuals. Reading NEET important topics is helpful as it saves time and prepares you for the important topics.
Just keep one thing in mind, study limited books as too many books can create confusion. Follow books which follow the latest NEET Biology syllabus of the year 2021.
Given below are some of the suggested books for NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus along with their publisher-
| Book name | Publisher | ISBN |
| Objective NCERT at your Fingertips for NEET-AIIMS – Biology | MTG Learning Media (P) Limited | 938656193X |
| Trueman’s Objective Biology for NEET | Trueman Book Company | 818722374X |
| NEET-AIPMT Biology 25 Years Chapterwise Solved Papers (1992-2017) By Career Point Kota | Career Point Publication | B01N9IQI7W |
| Master the NCERT Biology | Arihant Publication | 9311123862 |
| NCERT Xtract – Objective Biology for Class 11 & 12, AIPMT, AIIMS, JIPMER, BHU, AMU, State PMTs 2nd Edition | Disha Publication | 9385576380 |
| Objective Life Science (Plant Science) | S. Chand Publishing | 9352533674 |
The better you prepare for NEET, the better is your score and better placement in the college of your choice. It is important to give full commitment to the NEET 2021 Biology syllabus. The time allotted to this section should be merely 70 to 80 minutes, giving equal time to both Zoology and Botany sections independently. Biology requires direct knowledge and lease calculations. The quickest way to complete the NEET Biology section is not spending time thinking about a question. In Biology, facts do not work on logic, hence, you either know the answer or you don’t. There is no way you can ‘solve’ the answer in Biology. So, open your books and start learning!
NEET 2021 Exam Pattern: Check Latest Marking Scheme, No. of Questions and Detailed Analysis
NTA has released the updated exam pattern for NEET 2021. Detailed information related to marking scheme, number of questions, exam mode, exam duration, question type, the language of paper etc. have been released in the information brochure published by NTA. Candidates can get all the required information about the modified exam pattern from this article.
- NEET mode of examination: NEET 2021 is an offline test that will contain 200 MCQ, out of which 180 questions have to be attempted. There will be internal choice in questions. Each question will carry 4 marks each. The mode of the exam will be pen and paper. First, the aspirants will get a rough booklet and then they will have to mark the code of the test booklet on the OMR sheet.
- NEET Total marks: 720
- NEET syllabus: The NEET 2021 Syllabus covers the topics of Class XI and XII syllabus. Entire Syllabus is broadly divided into three sections: Physics, Chemistry, Biology (Botany and Zoology). Syllabus has not been reduced.
- Medium of NEET 2021 Question Paper: NEET 2021 will be conducted in 13 different languages. They are English, Tamil, Gujarati, Telugu, Assamese, Hindi, Oriya, Marathi, Kannada, Malayalam, Punjabi, Urdu and Bengali.
Check NEET Previous Year Question Paper.
- Marking scheme of NEET 2021 Exam: Candidates will get +4 marks for every correct answer, and -1 marks for each wrong answer.
- NEET Exam Duration: The candidates will get 3 hours time to attempt questions. For getting an idea about the questions, you can check NEET Sample Papers.

NEET 2021 Exam Pattern Overview
Let’s take a look at some key details about NEET Exam Pattern 2021-
| RESULT OF QUESTION | IMPACT |
| Popularly known as | NEET 2021 |
| Conducted by | NTA, MCI |
| Official website | ntaneet.nic.in |
| Total Number of questions | 200 |
| Number of questions to be Attempted | 180 |
| Type of questions | Multiple choice questions (MCQs) |
| Mode of examination | Offline (Pen and paper based) |
| Sections | Four (Physics, Chemistry, Botany and Zoology) |
| Total score | 720 |
| Duration of exam | 3 hours |
| Negative marking | Yes (-1 mark) |
Also Check
Number of Questions and Section-Wise Marks Distribution
As per NEET Exam Pattern, all the sections will be divided into Section A and B. All questions from Section A will be compulsory while Section B will have 15 questions, out of which candidates will be required to attempt any 10. The aspirants have to answer a total of 180 questions.
| Section | No. of Question |
| Physics | Section A: 35 Section B: 15 |
| Chemistry | Section A: 35 Section B: 15 |
| Biology(Zoology + Botany) | |
| Botany | Section A: 35 Section B: 15 |
| Zoology | Section A: 35 Section B: 15 |
| Total | 200 |
NEET 2021 Exam Pattern: Marking Scheme
Candidates can score +4 marks for each correct answer. There will be a negative marking. 1 mark will be deducted for every incorrect answer.
- No marks will be deducted if the candidate does not attempt the question.
- It is necessary to use a blue/black ball point pen to mark the answer.
- You should not mark more than one answer into the OMR sheet. It will lead you towards negative marking.
The marking scheme has been given in a simplified manner in the table below:
| RESULT OF QUESTION | IMPACT |
| Correct Answer | +4 marks |
| Incorrect Answer | -1 mark |
| Not Answered | 0 marks |
Check Out
NEET 2021 Exam Pattern: Language Option
NEET 2021 question paper will be provided in 13 languages. The default language is English. However, the candidates can also choose their regional language at the time of filling the NEET 2021 Application form.
The table given below shows different languages in which the exam is offered:
| HINDI | ENGLISH |
| ASSAMESE | BENGALI |
| GUJARATI | KANNADA |
| MARATHI | ODIA |
| TAMIL | TELUGU |
| PUNJABI | MALAYALAM |
| URDU | – |
- Candidates can choose their preferred language at the time of filling the NEET 2021 Application form. The aspirants cannot do any modification after the final submission of form even during the application form correction window.
- Candidates opting for English language will be given question papers in English only.
- Candidates opting for language other than English will be given a bilingual question paper. The candidates can choose English and any other language.
- Selection of regional/vernacular languages is subject to their respective state limits. Language of a particular region cannot be opted in any other region.
Options of languages, as per their respective region, are shown below:-
| Medium | Examination Centers |
| English | All over India |
| English and Hindi | All over India |
| English and Assamese | Exam Centers in Assam |
| English and Bengali | Exam Centers in West Bengal, Anadaman and Nicobar Islands, Tripura |
| English and Gujarati | Exam Centers in Gujarat, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu |
| English and Marathi | Exam Centers in Maharashtra |
| English and Tamil | Exam Centers in Tamil Nadu, Anadaman and Nicobar Islands and Puducherry |
| English and Telugu | Exam Centers in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana |
| English and Malayalam | Exam Centres in Kerala and Lakshadweep |
| English and Punjabi | Exam Centres in Punjab, Delhi and Chandigarh |
| English and Kannada | Exam Centers in Karnataka |
| English and Odia | Exam Centers in Odisha |
| English and Urdu | All Over India |
Check out
How to Calculate NEET Score?
The process for calculating NEET 2021 score is given below.
- NEET score= (Correct answers*4)-(Incorrect answers*1)
- Normalization method is used for nullifying the effects of varying difficulty level of question papers in different exam sessions.
NEET Paper Analysis
As per the analysis of NEET previous years question papers, the aspirants should go through the section wise observations:
Physics Paper Analysis
- Physics is considered to be the most difficult section in the NEET exam.
- Most weightage carrying section in Physics is Mechanics
- You might get 9-10 questions from electrodynamics
- Most of questions from this section will be lengthy and will involve calculations
- It is difficult to remember all the formulas. Hence, note it down in one place and read it regularly to memories them with ease.
Pro tip: Do not leave the ‘Points to Ponder’ section at the end of every chapter. You should practice the examples of NCERT books.
Chemistry Paper Analysis
- Chemistry questions are moderately difficult sections in the NEET exam.
- The aspirants might face more application based questions.
- Last year, students had to answer more questions from class XII NEET exam syllabus.
- The weightage of organic chemistry is more than the inorganic chemistry. Approximately 16-17 questions come from organic chemistry.
- Few of the questions are coming from two different concepts (together).
Pro Tip: The aspirants should give added attention for coordination compounds and chemical bonding. These sections carry most of the weightage. To clear your concept, read NCERT thoroughly.
Biology Paper Analysis
- Compared to the other two sections, Biology is the easiest one in NEET exam
- The students will face 45 questions from each section, Zoology and Botany
- Maximum questions of Biology are asked from NCERT. Hence, you should give extra attention to it instead of spending much time on the reference books.
Pro Tip: Human Physiology has a high weightage. Apart from this, Genetics will be another important chapter. Both the chapters cover approximately 30 questions in Biology.
You Might Like
NEET Exam Pattern And Syllabus
The following tables highlight the NEET 2021 Syllabus in a detailed manner:
NEET 2021 Physics Syllabus
| Physics – Class 11th | Physics – Class 12th |
| Work, Energy and Power | Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation |
| Properties of Bulk Matter | Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents |
| Physical world and measurement | Atoms and Nuclei |
| Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory | Electronic Devices |
| Laws of Motion | Current Electricity |
| Thermodynamics | Electrostatics |
| Oscillations and Waves | Electromagnetic Waves |
| Kinematics | Optics |
| Properties of Bulk Matter | Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism |
| Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body | – |
Check
- Preparation Tips to Ace Physics section
- Online Study Material for Physics Section
- NEET 2021: Preparation Tips and Strategies
NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus
| Chemistry – Class 11th | Chemistry – Class 12th |
| Structure of Atom | Polymers |
| Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Chemistry in Everyday Life |
| Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen |
| Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Biomolecules |
| Thermodynamics | Current Electricity |
| States of Matter: Gases and Liquids | Electrostatics |
| Redox Reactions | Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers |
| Equilibrium | Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acid |
| s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline earth metals) | Coordination Compounds |
| Hydrogen | Haloalkanes and Haloarenes |
| Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques | d and f Block Elements |
| Some p-Block Elements | p-Block Elements |
| Environmental Chemistry | Surface Chemistry |
| Hydrocarbons | General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements |
| Solid State | – |
| Solutions | – |
Read
NEET 2021 Biology Syllabus
| Biology – Class 11th | Biology – Class 12th |
| Structural Organization in Animals and Plants | Genetics and Evolution |
| Plant Physiology | Biotechnology and Its Applications |
| Diversity in Living World | Reproduction |
| Cell Structure and Function | Biology and Human Welfare |
| Human Physiology | Ecology and environment |
Check
NEET 2021 Important Topics
To meet the NEET 2021 cut off, you should prepare yourself by prioritizing the study schedule. The candidates should emphasize more on the heavy weightage sections. Find the following section to identify the most important topics of each subject:
Important Topics of Physics in NEET 2021
The most important six topics in Physics section are:
- Rigid Body Dynamics
- Electrodynamics
- KTG & Thermodynamics
- Semiconductors
- Modern Physics
- Wave Optics
Important Topics of Chemistry in NEET 2021
The syllabus of organic chemistry has been increased and has more prominence compared to inorganic chemistry.
- Coordination Compounds
- Organic Chemistry- I
- Chemical Bonding
- Carbonyl Compounds
Important Topics of Biology in NEET 2021
It is known that Biology covers both the Zoology and Botany subjects. Most of the questions of Biology are coming from NCERT.
- Excretory and Nervous System
- Pollination
- Photosynthesis
- Digestive system
- DNA Replication
- Plant Anatomy
- PAGE Theory
- Endocrine System
Also Check NEET Best Books for NEET 2021 Exam Preparation
NEET 2021 Important Instructions
Since NEET 2021 Exam is going to be held once in a year, candidates are advised not to make any silly mistakes that can make them ineligible to appear in NEET 2021.
- Timing of NEET 2021 is from 2 pm to 5 pm
- Entry to the examination hall will start at 12:30 pm. Candidates are advised to reach as early as possible, so that no issue arises. And if there is any issue, it can be solved within stipulated time
- No entry will be allowed after 1:30 pm
- The invigilators will check the candidates admit card and documents from 1:30 pm to 1:45 pm
- The NEET 2021 question papers will be distributed at 1:45 pm
- Rough work has to be done in the test booklet only.
- Candidate must have NEET 2021 Admit Card, passport size photograph and post card size photograph to enter in the examination hall
- There is no provision of re-checking of answer sheet
Also check
Instructions to Fill OMR Sheet in NEET 2021 Exam
- To answer the question, the aspirants should fill the OMR sheet with the help of Ball pen. It will be given to them from the exam center.
- Do not forget to mark the test booklet code on the top of the OMR sheet.
- To do rough work, the students should use the space of the test booklet. You should not write anything on the OMR sheet.
- You will not be allowed to change the answers in the OMR Sheet. Also, do not try to erase any information printed on the OMR sheet, otherwise your test might get cancelled.
Check
NEET 2021 Exam Pattern: Frequently Asked Question
Ques: What is the basic exam pattern for NEET 2021?
Ans: The exam pattern for NEET 2021 comprises of various factors given below:
- Exam Mode: Offline (pen and paper based)
- Number of Question: 200
- Number of Questions to be Attempted: 180
- Type of Question: Objective type(there will be four options for each question out of which only one would be the correct answer).
- Exam Duration: 3 hours
- Subjects: Physics, Chemistry, Biology(Botany and Zoology)
- Question Paper Language: 13 languages English, Hindi, Tamil, Assamese, Oriya, Kannada, Bengali, Gujarati, Malayalam, Punjabi, Marathi, Telugu and Urdu.
Ques: What is the marking scheme for NEET 2021?
Ans: NEET 2021 marking scheme includes all the marking factors of the exam:
- Total Marks: 720
- Marking Scheme: Four marks will be granted for every correct answer
NEET Negative Marking: One mark will be deducted for each incorrect answer.
Ques: How many answers could be marked for one question?
Ans: Candidates can mark only one answer for one question. Marking multiple answers can lead to negative marking.
Ques: Which color pen can candidates use to mark their answers?
Ans: Candidates can either use blue or black ball point pen to mark their answers. If they fail to do so, they might be disqualified.
Ques: How many MBBS seats are vacant in India?
Ans: As per the data delivered by MCI (Medical Council of India), there are 462 colleges offering MBBS and there are about 63835 seats.
Ques: Are there any changes made by NTA in the exam pattern for NEET 2021 examination?
Ans: Yes, NEET 2021 has been changed and internal choices have been introduced.
Ques: For how long the result of NEET 2021 is valid?
Ans: NEET 2021 result will hold its validity for the academic session 2021-2022 only.
Ques: If a student has opted for Hindi or vernacular language in NEET 2021 Test paper, in which language Test Paper will be provided to them?
Ans: In such cases, students will be provided with the test paper in their chosen language and English. In case of any ambiguity in the distributed paper, English version shall be treated as final.
Ques: How many attempts can a candidate make for the NEET exam?
Ans: On the proposal of the Union Health Ministry, MCI now has approved to remove the number of attempts limit from 2020 for NEET entrance examination. There is no cap limit for attempts.
Ques: How many sets of question papers will be distributed for NEET 2021?
Ans: As per the revised rules by MCI and supreme court order, there will be one set for question papers in all languages for NEET 2021.
Ques: What could not be worn for NEET 2021, particularly to avoid cheating?
Ans: Students are not allowed to wear shoes, sunglasses, full sleeves clothes, watches, bracelets, any sort of jewelry, saree and cap. They might get pointed out by the on-duty invigilator who can take actions as per the norms.
Ques: What is the minimum cut off percentile for candidates from all categories?
Ans: Minimum 50% cut off is required for general category candidates whereas 40% cut off is needed for SC/ST/OBC candidates to qualify.