Home » Posts tagged 'NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus'
Tag Archives: NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus
NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus – Check Detailed Syllabus and Important Topics
NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus is very vast and can be classified into three parts, namely- Physical, Organic and Inorganic Chemistry. NEET 2021 covers Chemistry Syllabus as prescribed in CBSE class XI and class XII NCERT books. The students have to answer 45 questions in the NTA NEET 2021 Chemistry section. Check NEET 2021 Exam pattern.
NTA has not published an official notice related to changes in NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus. So it is pretty clear that the NTA NEET 2021 Chemistry syllabus would be similar to NEET Syllabus 2020.
The best NEET 2021 preparation tips for Chemistry Syllabus is to prepare the top 10 important topics of NEET Chemistry Syllabus thoroughly along with that you can start devising your self-study plan. The more time you allot to the high weightage chapters higher will be your score in NTA NEET 2021 chemistry section. Not to forget, the more the revision, the better is the performance. Check NEET 2021 Revision Plan.
NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus– Chapters
Find the following table to identify the important topics of NEET Chemistry Syllabus:
| Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Laws of Chemical Combination |
| Structure of Atom, Atomic Number | Isotopes & Isobars |
| Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Ionic Bond |
| Covalent Bond | States of Matter: Gases and Liquids |
| Thermodynamics | Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties |
| Electronegativity | Equilibrium |
| Equilibrium in Physical & Chemical Process | Redox Reactions |
| Hydrogen | Physical & Chemical Properties of Water |
| S-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline earth metals) | Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles and Techniques |
| Some p-Block Elements | Hydrocarbons |
| Environmental Chemistry | Solid State |
| Band Theory of Metals | Solutions |
| Elevation of Boiling Point | Chemical Kinetics |
| Surface Chemistry | General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements |
| Electrochemistry | p-Block Elements |
| d and f Block Elements | Haloalkanes and Haloarenes |
| Alcohols | Physical & Chemical Properties of Primary Alcohol |
| Phenols and Ethers | Coordination Compound |
| Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen |
| Amines, Cyanides & Isocyanides | Polymers |
| Biomolecules | Chemistry in Everyday Life |
| Cleansing Agents – Soaps & Detergents | – |
Click here for NEET 2021 Syllabus of Biology
Detailed Class 11th NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus
Given below is the detailed NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus from Class 11th. The syllabus can be saved using Ctrl + P (Print) option to download the NEET Chemistry Syllabus PDF.
UNIT I: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Atomic and molecular masses
- Laws of chemical combination, Dalton’s atomic theory: concept of elements, atoms and molecules
- General Introduction: Important and scope of chemistry
- Mole concept and molar mass; percentage composition and empirical and molecular formula; chemical reactions, stoichiometry and calculations based on stoichiometry
UNIT II: Structure of Atom
- Atomic number, isotopes and isobars. Concept of shells and subshells, dual nature of matter and light, de Broglie’s relationship, Heisenberg uncertainty principle, concept of orbital, quantum numbers, shapes of s,p and d orbitals, rules for filling electrons in orbitals- Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principles and Hund’s rule, electronic configuration of atoms, stability of half filled and completely filled orbitals.
UNIT III: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Modern periodic law and long form of periodic table, periodic trends in properties of elements- atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, electronegativity, valence.
UNIT IV: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Valence electrons, ionic bond, covalent bond, bond parameters, Lewis structure, polar character of covalent bond, valence bond theory, resonance, geometry of molecules, VSEPR theory, concept of hybridization involving s, p and d orbitals and shapes of some simple molecules, molecular orbital theory of homonuclear diatomic molecules (qualitative idea only). Hydrogen bond.
UNIT V: States of Matter: Gases and Liquids
- Three states of matter, inter molecular interactions, types of bonding, melting and boiling points, role of gas laws of elucidating the concept of the molecule, Boyle’s law, Charle’s law, Gay Lussac’s law, Avogadro’s law, ideal behavior of gases, empirical derivation of gas equation.
- Avogadro number, ideal gas equation. Kinetic energy and molecular speeds (elementary idea), deviation from ideal behavior, liquefaction of gases, critical temperature. Liquid State- Vapour pressure, viscosity and surface tension (qualitative idea only, no mathematical derivations).
UNIT VI: Thermodynamics
- First law of thermodynamics-internal energy and enthalpy, heat capacity and specific heat, measurement of U and H, Hess’s law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of: bond dissociation, combustion, formation, atomization, sublimation, phase transition, ionization, solution and dilution
- Introduction of entropy as state function, Second law of thermodynamics, Gibbs energy change for spontaneous and non-spontaneous process, criteria for equilibrium and spontaneity
- Third law of thermodynamics- Brief introduction
UNIT VII: Equilibrium
- Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes, dynamic nature of equilibrium, law of chemical equilibrium, equilibrium constant, factors affecting equilibrium-Le Chatelier’s principle; ionic equilibrium- ionization of acids and bases, strong and weak electrolytes, degree of ionization, ionization of polybasic acids, acid strength, concept of PH., Hydrolysis of salts (elementary idea), buffer solutions, Henderson equation, solubility product, common ion effect (with illustrative examples)
UNIT VIII: Redox Reactions
- Concept of oxidation and oxidation and reduction, redox reactions oxidation number, balancing redox reactions in terms of loss and gain of electron and change in oxidation numbers
UNIT IX: Hydrogen
- Occurrence, isotopes, preparation, properties and uses of hydrogen; hydrides-ionic, covalent and interstitial; physical and chemical properties of water, heavy water; hydrogen peroxide-preparation, reactions, uses and structure
UNIT X: s-Block Elements (Alkali and Alkaline earth metals)
- General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, anomalous properties of the first element of each group
- Group I and group 2 elements: diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties (such as ionization enthalpy, atomic and ionic radii), trends in Sodium carbonate, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide and sodium hydrogen carbonate, biological importance of sodium
- Preparation and Properties of Some important Compounds: chemical reactivity with oxygen, water, hydrogen and halogens; uses. Industrial use of lime and limestone, biological importance of Mg and Ca and potassium
UNIT XI: Some p-Block Elements
- General Introduction to p-Block Elements
- Group 13 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, variation of properties, oxidation states, trends in chemical reactivity, anomalous properties of the first element of the group; Boron, some important compounds: borax, boric acids, boron hydrides. Aluminium: uses, reactions with acids and alkalis
- General 14 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, variation of properties, oxidation states, trends in chemical reactivity, anomalous behavior of the first element. Carbon, allotropic forms, physical and chemical properties: uses of some important compounds: oxides
- Important compounds of silicon and a few uses: silicon tetrachloride, silicones, silicates and zeolites, their uses
UNIT XII: Organic Chemistry- Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- General introduction, methods of purification, qualitative and quantitative analysis, classification and IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds.
- Electronic displacements in a covalent bond: inductive effect, electromeric effect, resonance and hyperconjugation
- Homolytic and heterolytic fission of a covalent bond: free radials, carbocations, carbanions; electrophiles and nucleophiles, types of organic reactions.
UNIT XIII: Hydrocarbons
- Alkanes: Nomenclature, isomerism, conformations (ethane only), physical properties, chemical reactions including free radical mechanism of halogenation, combustion and pyrolysis.
- Alkanes: Nomenclature, structure of double bond (ethene), geometrical isomerism, physical properties, methods of preparation: chemical reactions: addition of hydrogen, halogen, water, hydrogen halides (Markovnikov’s addition and peroxide effect), ozonolysis, oxidation, mechanism of electrophilic addition.
- Alkynes: Nomenclature, structure of triple bond (ethyne), physical properties, methods of preparation, chemical reactions: acidic character of alkynes, addition reaction of- hydrogen, halogens, hydrogen halides and water.
- Aromatic hydrocarbons: Introduction, IUPAC nomenclature; Benzene; resonance, aromaticity; chemical properties: mechanism of electrophilic substitution- Nitration sulphonation, halogenation, Friedel Crafts alkylation and acylation; directive influence of functional group in mono-substituted benzene; carcinogenicity and toxicity.
UNIT XIV: Environmental Chemistry
- Environmental pollution: Air, water and soil pollution, chemical reactions in atmosphere, smogs, major atmospheric pollutants; acid rain ozone and its reactions, effects of depletion of ozone layer, greenhouse effect and global warming- pollution due to industrial wastes; green chemistry as an alternative tool for reducing pollution, strategy for control of environmental pollution
Click here for NEET 2021 Syllabus of Physics
Detailed Class 12th NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus
UNIT I: Solid State
- Classification of solids based on different binding forces; molecular, ionic covalent and metallic solids, amorphous and crystalline solids (elementary idea), unit cell in two dimensional and three-dimensional lattices, calculation of density of unit cell, packing in solids, packing efficiency, voids, number of atoms per unit cell in a cubic unit cell, point defects, electrical and magnetic properties, Band theory of metals, conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
UNIT II: Solutions
- Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids, solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, colligative properties- relative lowering of vapour pressure, Raoult’s law, elevation of boiling point, depression of freezing point, osmotic pressure, determination of molecular masses using colligative properties abnormal molecular mass. Van’t Hoff factor.
UNIT III: Electrochemistry
- Redox reactions, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar conductivity variation of conductivity with concentration, kohlrausch’s Law, electrolysis and Laws of electrolysis (elementary idea), dry cell- electrolytic cells and Galvanic cells; lead accumulator, EMF of a cell, standard electrode potential, Relation between Gibbs energy change and EMF of a cell, fuel cells; corrosion.
UNIT IV: Chemical Kinetics
- Rate of a reaction (average and instantaneous), factors affecting rates of reaction; concentration, temperature, catalyst; order and molecularity of a reaction; rate law and specific rate constant, integrated rate equations and half life (only for zero and first order reactions); concept of collision theory ( elementary idea, no mathematical treatment). Activation energy, Arrhenious equation.
UNIT V: Surface chemistry
- Adsorption– Physisorption and chemisorption; factors affecting adsorption of gases on solids, catalysis homogeneous and heterogeneous, activity and selectivity: enzyme catalysis; colloidal state: distinction between true solutions, colloids and suspensions; lyophilic, lyophobic multimolecular and macromolecular colloids; properties of colloids; Tyndall effect, Brownian movement, electrophoresis, coagulation; emulsions- types of emulsions.
UNIT VI: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Principles and methods of extraction- concentration, oxidation, reduction electrolytic method and refining; occurrence and principles of extraction of aluminium, copper, zinc and iron.
UNIT VII: p- Block Elements
- Group 15 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, oxidation states, trends in physical and chemical properties; preparation and properties of ammonia and nitric acid, oxides of nitrogen (structure only); Phosphorus- allotropic forms; compounds of phosphorus: preparation and properties of phosphine, halides (PCI3 , PCI5 ) and oxoacids (elementary idea only).
- Group 16 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties; dioxygen: preparation, properties and uses; classification of oxides; ozone. Sulphur – allotropic forms; compounds of sulphur: preparation, preparation, properties and uses of sulphur dioxide; sulphuric acid: industrial process of manufacture, properties and uses, oxoacids of sulphur (structures only).
- Group 17 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties; compounds of halogens: preparation, properties and uses of chlorine and hydrochloric acid, interhalogen compounds oxoacids of halogens (structures only).
- Group 18 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties, uses.
UNIT VIII: d and f Block Elements
- General introduction, electronic configuration, characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first row transition metals- metallic character, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii, colour, catalytic property, magnetic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy formation. Preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4.
- Lanthanoids- electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical reactivity, and lanthanoid contraction and its consequences.
- Actinoids: Electronic configuration, oxidation states and comparison with lanthanide.
UNIT IX: Coordination Compounds
- Coordination compounds: Introduction, ligands, coordination number, colour, magnetic properties and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds, isomerism (structural and stereo) bonding, Werner’s theory VBT,CFT; importance of coordination compounds (in qualitative analysis, biological systems)
UNIT X: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Haloalkanes: Nomenclature, nature of C –X bond, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of substitution reactions, Optical rotation.
- Haloarenes: Nature of C-X bond, substitution reactions (directive influence of halogen for monosubstituted compounds Uses and environment effects of – dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, iodoform, freons, DDT only).
UNIT XI: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Alcohols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties (of primary alcohols only); identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols; mechanism of dehydration, uses with special reference to methanol and ethanol.
- Phenols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophilic substitution reactions, uses of phenols.
- Ethers: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties uses.
UNIT XII: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Aldehydes and Ketones: Nomenclature, nature of carbonyl group, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; and mechanism of nucleophilic addition, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes; uses.
- Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; uses.
UNIT XIII: Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses,identification of primary secondary and tertiary amine
- Cyanides and Isocyanides: will be mentioned at relevant places.
- Diazonium salts: Preparation, chemical reactions and importance in synthetic organic chemistry.
UNIT XIV: Biomolecules
- Carbohydrates: Classification (aldoses and ketoses), monosaccharide (glucose and fructose), D.L. configuration, oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen): importance.
- Proteins: Elementary idea of – amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides, proteins, primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure and quaternary structure (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins; enzymes.
- Hormones: Elementary idea (excluding structure).
- Vitamins: Classification and function.
- Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA
UNIT XV: Polymers
- Classification: Natural and synthetic, methods of polymerization (addition and condensation), copolymerization. Some important polymers: natural and synthetic like polyesters, bakelite; rubber, Biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers.
UNIT XVI: Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Chemicals in medicines: analgesics, tranquilizers, antiseptics, disinfectants, antimicrobials, antifertility drugs, antibiotics, antacids, antihistamines.
- Chemicals in food: preservatives, artificial sweetening agents, elementary idea of antioxidants.
- Cleansing agents: soaps and detergents, cleansing action.
Check Official NTA NEET 2021 Syllabus for Physics, Chemistry and Biology
Most Important Topics of NEET Chemistry Syllabus
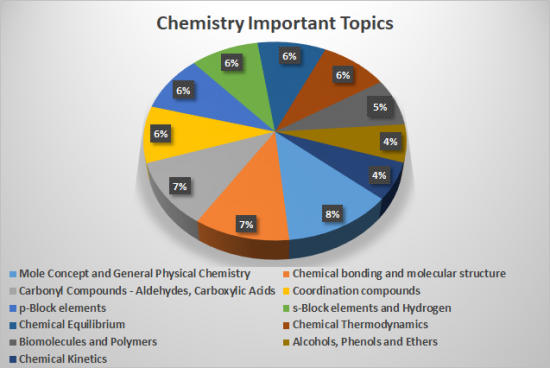
As stated before, NEET Chemistry Syllabus comes under 3 sub-sections – Physical, Organic and Inorganic Chemistry. All of these three sections have almost equal weightage. But it is also important to note that in each of these 3 sections, there are certain chapters which have much higher weightage and are thus very important. Nevertheless, candidates must give importance to every topic in the NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus. Some topics were asked repeatedly in NEET Previous Year Question Papers. Candidates can check the table mentioned below to understand the NEET 2021 Syllabus Weightage of Chemistry-
| Important Topics of NEET Chemistry Syllabus | Weightage (in percentage) |
| Mole Concept and General Physical Chemistry | 8% |
| Chemical bonding and molecular structure | 7% |
| Carbonyl Compounds – Aldehydes, Carboxylic Acids | 7% |
| Coordination compounds | 6% |
| p-Block elements | 6% |
| s-Block elements and Hydrogen | 6% |
| Chemical Equilibrium | 6% |
| Chemical Thermodynamics | 6% |
| Biomolecules and Polymers | 5% |
| Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers | 4% |
| Chemical Kinetics | 4% |
Read: Why NCERT books are important for NEET 2021 Preparation?
Weightage for NEET Chemistry Syllabus: Inorganic
| Topics | Questions | Total Marks |
| P and S block | 2 | 8 |
| Chemical Bonding | 5 | 20 |
| Periodic Table | 1 | 4 |
| D and F block | 2 | 8 |
| Coordination Compounds | 4 | 16 |
| Qualitative Analysis | 1 | 4 |
| Metallurgy | 1 | 4 |
| Total | 16 | 64 |
Weightage for NEET Physical Chemistry
| Topics | Questions | Total Marks |
| Chemical Equilibrium | 3 | 12 |
| Nuclear Chemistry and Atomic Structure | 1 | 4 |
| Thermochemistry and Thermodynamics | 2 | 8 |
| Mole Concept | 1 | 4 |
| Electrochemistry | 1 | 4 |
| Chemical Kinetics | 2 | 8 |
| Solution and Colligative Properties | 1 | 4 |
| Solid State | 1 | 4 |
| Surface Chemistry | 1 | 4 |
| Total | 13 | 52 |
Read More
Weightage for NEET Chemistry Syllabus: Organic
| Topics | Questions | Total Marks |
| Alkyl Halide, Alcohol and Ether | 2 | 8 |
| General Organic Chemistry | 3 | 12 |
| Biomolecules | 1 | 4 |
| Aromatic Compounds | 1 | 4 |
| Chemistry in Everyday Life | 1 | 4 |
| Carbonyl Compounds | 4 | 16 |
| IUPAC & Isomerism | 2 | 8 |
| Environmental Chemistry | 1 | 4 |
| Practical Organic Chemistry | 1 | 4 |
| Total | 16 | 64 |
NEET 2021 Preparation Tips For Chemistry
NEET questions are generally simple. Although the NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus is wide and has too much to study, the questions are repetitive and with a simple twist. Practicing regularly with NEET Previous Year Question Papers will help improve the performance by a large margin. Additionally, the candidates need to be quick and wise in the selection of questions to clear the exam with a good score.
Also Check | NEET 2021 Sample Papers
Given below are some tips to improvise the learning of NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus-
Best NEET 2021 Preparation Tips for Chemistry Syllabus
- Solve, Learn and Practice: The key to success in the NEET 2021 chemistry section is practicing maximum questions. Solve the questions on your own at first attempt, learn from the mistakes and practice more of such questions.
- Practice Papers and Mock Tests: It is important to attempt maximum NEET mock tests or practice papers for NEET. Watch video lectures over how to attempt the NEET 2021 Chemistry section the right way and learn the strategy of toppers.
- Inorganic chemistry must be learned throughout the year: As inorganic chemistry has a vast syllabus and difficult structural diagrams, best to practice them regularly.
- NCERT is your X-Factor: NEET questions are mostly asked directly from specific lines of a specific chapter, so try to by heart the concepts with line.
- Reference books: Along with NCERT books candidates must refer some other books that give you space for practice.
- Last day preparation: Make a small pocket manual for yourself where you can keep all the important concepts handy, or a collection of information that can be used for studying the important topics of NEET Chemistry Syllabus at the last minute.
- Never try new things in the last few days: As the NEET 2021 Syllabus of Chemistry is quite vast. This requires you to follow a timetable and study things with some gaps and space, but do not learn anything new in the last few days, if you have not worked with it previously.
- Last minute revision: Revision is an important part of the syllabus, so just revise everything you have learned in the last few days.
- Take care of your health: Best to eat small meals at regular intervals to keep your mind fresh. Take proper sleep of at least 6 hours!
Check Complete NEET 2021 Preparation Tips
NTA Video Lectures For NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus
On the official portal of NTA, students can find video lectures by IIT-PAL which are watchable on mobile phones or tablets as well. The videos are uploaded on the IIT-PAL page on Youtube. There are more than 100 video lectures of about 50 to 60 minutes duration for each video. Lectures are divided according to topics of various chapters and are prepared by reputed faculty members of top IITs. To access these videos-
- Go to www.nta.ac.in
- Click on ‘Students’ tab
- Select Content Based Lectures under ‘Test Practice’ section
- Select Chemistry video lectures.
- New page on youtube will load showing a playlist of lectures.
Free NEET Mock Tests by NTA for NEET Chemistry Syllabus
NTA also provides free mock tests on the official portal. Students can head over to – www.nta.ac.in/quiz to access the Mock Tests. These mock tests can be attempted on a computer free of cost and also do not require any registration on the website. The papers given in these mock tests are of previous years of NEET examination. Section-wise mocks are available here so a student can focus on questions from NEET Chemistry Syllabus. It is advised to attempt the mocks once the whole syllabus is completed.
Best Books for NEET Chemistry Syllabus
Identify the best books for NEET Chemistry Syllabus suiting your study style and work with them at regular intervals, so that you are able to master the NEET Chemistry Syllabus in the due course of time.
MCQs for NEET Chemistry are generally not very difficult, except with a few exceptions. Students must stick to the best time management of work in order to perform best within the stipulated time period. Some good books for NEET Chemistry syllabus are as follows:
| Book name | Publisher | ISBN |
| A to Z Chemistry for NEET Class XI | Cengage Learning India Pvt Ltd | 8131534200 |
| Universal Self-Scorer Errorless Chemistry (Set of 2 Volumes) | Universal Books Depot | 8193000218 |
| Marvel Chemistry MCQs Volume 2 For NEET(UG) And JEE (Main) Exams | Marvel Publication | 8193371747 |
| Objective Chemistry – Chapter-wise MCQ for JEE Main/ BITSAT/ AIPMT/ AIIMS/ KCET 2nd Edition | Disha Publications | 9385576712 |
As stated all over this article, NEET 2021 Chemistry Syllabus is vast but not exactly difficult. Only the student should keep practicing consistently and with full dedication. It is important to stick with the NEET Chemistry Syllabus and the NEET 2021 exam pattern. Keep in mind that there is negative marking for every incorrect answer in NEET and OMRs do not have any option to change the answer!